INTRODUCTION
Urologists are increasingly using ureteral stents following endoscopic stone removal either by percutaneous nephrolithotomy or by ureteroscopy. Patients often experience severe morbidity as a result of their use such as pain, hematuria, storage and voiding lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).1 Majority of stents are removed under local an aesthesia and patients experience significant pain and anxiety during the double J (DJ) removal. A number of studies have been undertaken to assess the issues that can occur when a stent is removed.2 Diclofenac, a long-acting non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with a fast start of action, has been shown to be very successful in the treatment of renal colic.3 This medication works by suppressing the formation and release of prostaglandins, which helps to relieve pain during DJ removal. Tamsulosin is a medication that works as a selective alpha 1 blocker. Prostate, bladder, and ureter all have alpha 1 receptors. Tamsulosin can help to minimise ureteral contractions as well as irritation in the trigonal area. A single dose of a NSAID was used by Tadros et al4 to prevent severe discomfort after the removal of a ureteral stent. In other studies, the combination of silodosin and diclofenac sodium was found to be useful in decreasing discomfort following ureteral stent removal.5 In patients with DJ-stents, the combination of tamsulosin and propiverine reduced irritative voiding symptoms, suprapubic pain, and improved quality of life.6 In study by Hadibrata et al7 tamsulosin along with diclofenac was found to be effective therapy to decrease pain after stent removal.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was done between October 2019 to March 2021. A total of 60 patients scheduled for outpatient DJ removal were included in the study. A 5 Fr DJ polyurethane ureteral stent was used in all of the patients. Before being removed, the DJ-stent was retained for 3-4-weeks. Participants were divided into three equal groups using a computer-based generated random number sequence before starting the study. Group-A included patients who were given placebo. Group-B included patients who were given diclofenac prior to DJ removal and Group-C included patients who were given combination therapy with diclofenac and tamsulosin two hours before procedure.
Inclusion Criteria
1. Age>18-years.
2. All patients with unilateral DJ-stent in situ following percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) or ureteroscopic lithotripsy (URSL).
Exclusion Criteria
1. Analgesic or sedative drugs used within at least 24-hours from the procedure.
2. Contraindications for the procedure (e.g., lidocaine allergy, urinary tract infection, anatomical problems related to the urethra).
Urine routine microscope was routinely performed before cystoscopy. Patient were given placebo (Multivitamin tablet) in Group-A, Diclofenac in Group-B and Diclofenac and Tamsulosin in Group-C 2-hours prior to DJ removal.
After taking informed consent from the patients, the patients were placed in a lithotomy position. Perineum was cleaned with povidine iodine, and 10 ml 2% lidocaine gel was then injected into the urethra. A 17 Fr rigid cystoscope was used for all patients. No analgesic drugs were administered to the patients during the procedure.
Baseline vital parameters (pulse rate, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure) were documented before and during the procedure using pulse-oxymetry and non-invasive blood pressure monitoring. Subsequently, all these patients were given a visual analog scale (VAS) score sheet (Figure 1) to rate their pain sensation during the procedure on a scale of ranging from 0 to10 after the completion of procedure. We defined no pain as a score of 0, mild pain as a score of 1 to 3, moderate pain as a score of 4 to 7, and severe pain as a score of 8 to 10. Anxiety score were assessed using state trait anxiety scale (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Visual Analog Scale Score for Pain Sensation
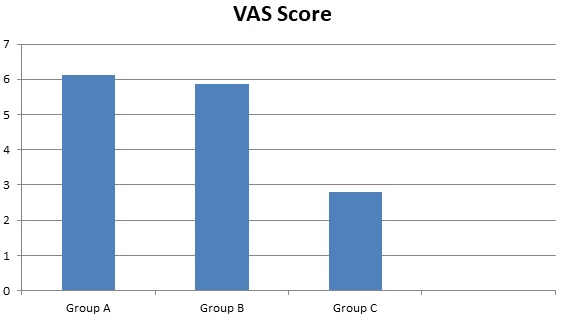
Figure 2. Median Anxiety Score as per State Trait Anxiety Scale
Number, percentage, mean, standard deviation and median were used for descriptive statistics of the data. Comparative analysis between two groups was performed using the Chi-square test for categorical data and independent t-test or Mann–Whitney U‑test for continuous data. p value less than 0.05 was considered as significant. Statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) software was used for analysis (version 20, IBM Corporation, NY, and USA).
RESULT
A total of 60 patients were included. No participants withdrew from the study.
General Characteristic
The mean (±standard deviation) patient age was 36.5±9.3-years in Group-A and 38.8±10.6 in Group-B and 35.4±10.2 in Group-C. The age distribution among groups were comparable without any significant differences. There was no statistical significant difference between the two groups in terms of body mass index, and educational status (p>0.05) (Table 1).
| Table 1. General Characteristic of the Participants |
|
Characteristic
|
Group A (n=20)
n% |
Group B (n=20)
n% |
Group C (n=20)
n%
|
| Age (Mean±SD) |
36.5±9.3
|
38.8±10.6 |
35.4±10.2
|
| BMI (Mean±SD) |
25.4±5.2
|
26.2±4.9 |
24.2±4.9
|
| Educational Status |
| Primary school |
10(50%)
|
12(60%) |
12(60%)
|
| Secondary school |
4(20%)
|
5(25%) |
4(20%)
|
| Higher education school |
6(30%)
|
3(15%) |
4(20%)
|
VAS Score, Anxiety Score and Hemodynamic Parameters Related to Cystoscopy
There was no statistical difference between duration of surgery. The mean duration of the procedure was 7.7±1.4-minutes in Group-A, 8.1±1.5-minutes in Group-B and 7.4±1.6-minutes in Group-C (p>0.05). Compared to the Group-A and Group-B, pain scores were significantly lower in Group-C (Table 2).
| Table 2. Comparison between Pain Score (VAS Score) |
|
Group A(n=20)
|
Group B(n=20) |
Group C(n=20) |
p Value
|
| VAS Score (after cystoscopy) |
6.12±1.85
|
5.87±1.47 |
2.80±1.47 |
<0.001
|
p<0.05 value is significant. Bold values are statistically significant.
Mann-Whitney U test |
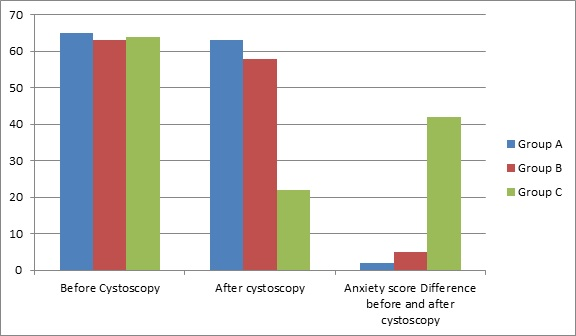
A statistically significant difference was found to be between the two groups in terms of anxiety scores before and after cystoscopy.
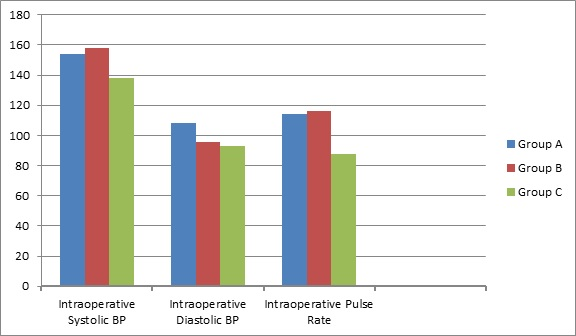
Anxiety scores before cystoscopy were similar in all groups, but anxiety scores after cystoscopy were significantly lower in Group-C than the Group-A and Group-B (Table 3). Statistically significant differences were also found between the Group-C and the Group-A and B in terms of intraoperative systolic pressure and pulse rate. These parameters were significantly lower in the Group-C (Table 4).
| Table 3. Median Anxiety Score before and after Procedure |
|
Group A (n=20)
|
Group B (n=20) |
Group C (n=20) |
p Value
|
| Before cystoscopy |
65.0
|
63.0 |
64.0 |
0.08
|
| After Cystoscopy |
63.0
|
58.0 |
22.0 |
<0.001
|
| Anxiety Score difference before and after cystoscopy |
2.0
|
5.0 |
42.0 |
<0.001
|
p<0.05 value is significant. Bold values are statistically significant.
Mann-Whitney U test |
| Table 4. Median Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate before and During Procedure |
|
Group A(n=20)
|
Group B(n=20) |
Group
C(n=20) |
p Value
|
| Preoperative Systolic BP (mm Hg) |
134
|
136 |
130 |
0.78
|
| Preoperative Diastolic BP (mm Hg) |
90
|
90 |
94 |
0.82
|
| Preoperative Pulse Rate |
86
|
86 |
86 |
0.68
|
| Intraoperative Systolic BP |
154
|
158 |
138 |
0.018
|
| Intraoperative Diastolic BP |
108
|
96 |
93 |
0.72
|
| Intraoperative Pulse rate |
114
|
116 |
88 |
<0.001
|
p<0.05 value is significant. Bold values are statistically significant.
Mann-Whitney U test. |
DISCUSSION
The patients planned for DJ removal are often worried about the pain associated with the procedure and frequently enquire regarding the measures that would be undertaken for pain relief during the procedure. Several studies have been conducted to reduce stentrelated pain and discomfort using drugs such as alpha blockers, anticholinergics, and phosphodiesterase inhibitors, as well as new stent designs, stent materials, and stent dimensions.8,9,10,11,12
In our study groups were comparable to age, body mass index (BMI) and educational status. Operative time was also comparable in all groups. VAS scored decreased significantly in patients who received combination therapy with diclofenac and tamsulosin. There was significant reduction of anxiety on state trait anxiety scale. Systolic BP, diastolic BP and pulse rate were comparable in all groups before procedure however during the procedure a statistically significant difference was found in these parameters (Except diastolic BP).
CONCLUSION
Combination therapy with tamsulosin and diclofenac reduces subjective pain sensation and there is an objective change in the sympathetic response to pain as demonstrated by the change in vital parameters.
This is a simple method to decrease pain, anxiety and hemodynamic parameters (Figure 3) in patients undergoing DJ removal.
Figure 3. Median Hemodynamic Parameters during Cystoscopy
LIMITATION
DJ removal was not done by same urologist in every patient. Pain score and anxiety score were assessed immediately after DJ removal and patient were not followed-up for development of any symptoms. Finally, objective assessment is difficult because pain is subjective.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.








