1. Stejskal EO, Tanner JE. Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. Journal of Chemical Physics. 1965; 42(1): 288-292. doi: 10.1063/1.1695690
2. Basser PJ, Mattiello J, Lebihan D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J. 1994; 66(1): 259-267. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80775-1
3. Thomason ME, Thompson PM. Diffusion imaging, white matter, and psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011; 7: 63-85. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104507
4. Mori S, Zhang J. Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its applications to basic neuroscience research. Neuron. 2006; 51(5): 527-539. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.012
5. Sporns O. The human connectome: a complex network. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1224: 109-125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05888.x
6. Li H, Xue Z, Cui K, Wong ST. Diffusion tensor-based fast marching for modeling human brain connectivity network. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2011; 35(3): 167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2010.07.008
7. Steel RM, Bastin ME, Mcconnell S, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) in schizophrenic subjects and normal controls. Psychiatry Res. 2001; 106(3): 161-170. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2010.07.008
8. Hagmann P, Kurant M, Gigandet X, et al. Mapping human whole-brain structural networks with diffusion MRI. PLoS One. 2007; 2(7): e597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000597
9. Gong GL, He Y, Concha L, et al. Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cerebral Cortex. 2009; 19(3): 524-536. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn102
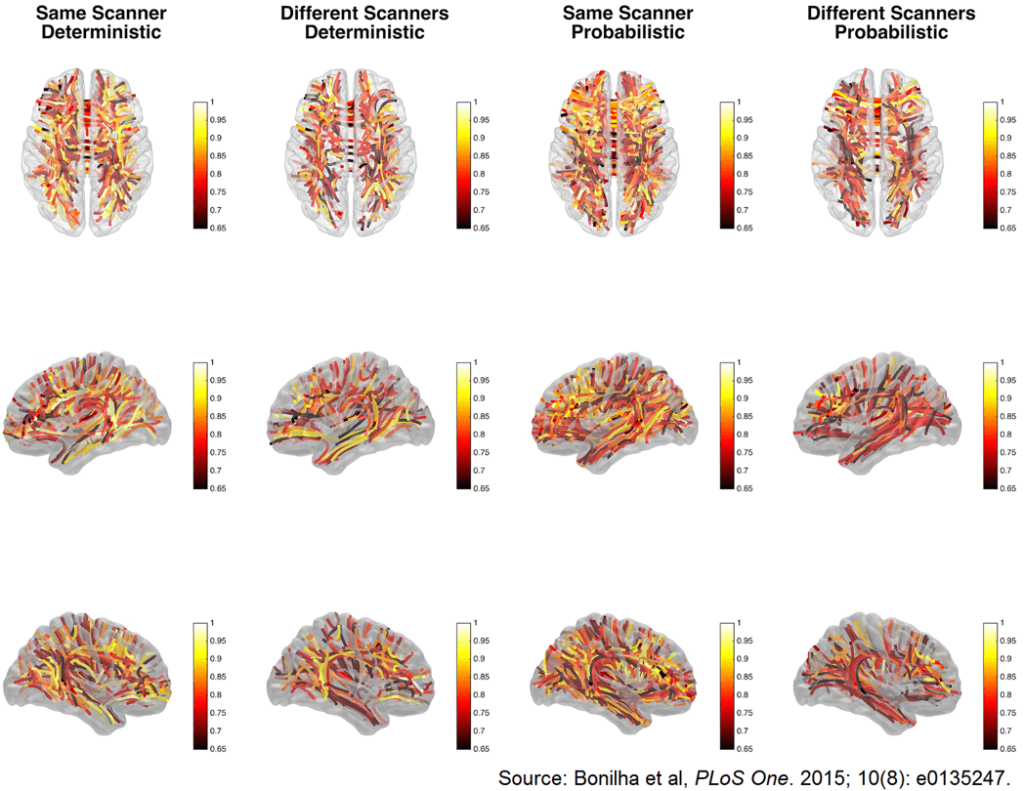
10. Bonilha L, Gleichgerrcht E, Fridriksson J, et al. Reproducibility of the structural brain connectome derived from diffusion tensor imaging. PLoS One. 2015; 10(8): e0135247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135247
11. Iturria-Medina Y, Sotero RC, Canales-Rodriguez EJ, Aleman-Gomez Y, Melie-Garcia L. Studying the human brain anatomical network via diffusion-weighted MRI and Graph Theory. Neuroimage. 2008; 40(3): 1064-1076. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.060
12. Arsiwalla XD, Dalmazzo D, Zucca R, et al. Connectomics to semantomics: addressing the brain’s big data challenge. Inns Conference on Big Data 2015 Program. 2015; 53: 48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.07.278
13. Holtzman DM, Morris JC, Goate AM. Alzheimer’s disease: the challenge of the second century. Sci Transl Med. 2011; 3(77): 77sr71. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002369
14. Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, et al. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6(8): 734-746. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70178-3
15. Goedert M, Spillantini MG. A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 2006; 314(5800): 777-781. doi: 10.1126/science.1132814
16. Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Flory J, Damasio AR, Van Hoesen GW. The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Cerebral Cortex. 1991; 1(1): 103-116. doi: 10.1093/cercor/1.1.103
17. Braak H, Braak E. Staging of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol Aging. 1995; 16(3): 271-278; discussion 278-284. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(95)00021-6
18. Rose SE, Chen F, Chalk JB, et al. Loss of connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease: an evaluation of white matter tract integrity with colour coded MR diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 69(4): 528-530. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.69.4.528
19. Medina DA, Gaviria M. Diffusion tensor imaging investigations in Alzheimer’s disease: the resurgence of white matter compromise in the cortical dysfunction of the aging brain. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008; 4(4): 737-742. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S3381
20. Fu JL, Liu Y, Li YM, Chang C, Li WB. Use of diffusion tensor imaging for evaluating changes in the microstructural integrity of white matter over 3 years in patients with amnesic-type mild cognitive impairment converting to Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimaging. 2014; 24(4): 343-348. doi: 10.1111/jon.12061
21. Ringman JM, O’neill J, Geschwind D, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in preclinical and presymptomatic carriers of familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations. Brain. 2007; 130(Pt 7): 1767-1776. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm102
22. Nir TM, Jahanshad N, Villalon-Reina JE, et al. Effectiveness of regional DTI measures in distinguishing Alzheimer’s disease, MCI, and normal aging. Neuroimage Clin. 2013; 3: 180-195. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.07.006
23. Stebbins GT, Murphy CM. Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Behav Neurol. 2009; 21(1): 39-49. doi: 10.3233/BEN-2009-0234
24. Chua TC, Wen W, Slavin MJ, Sachdev PS. Diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008; 21(1): 83-92. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e3282f4594b
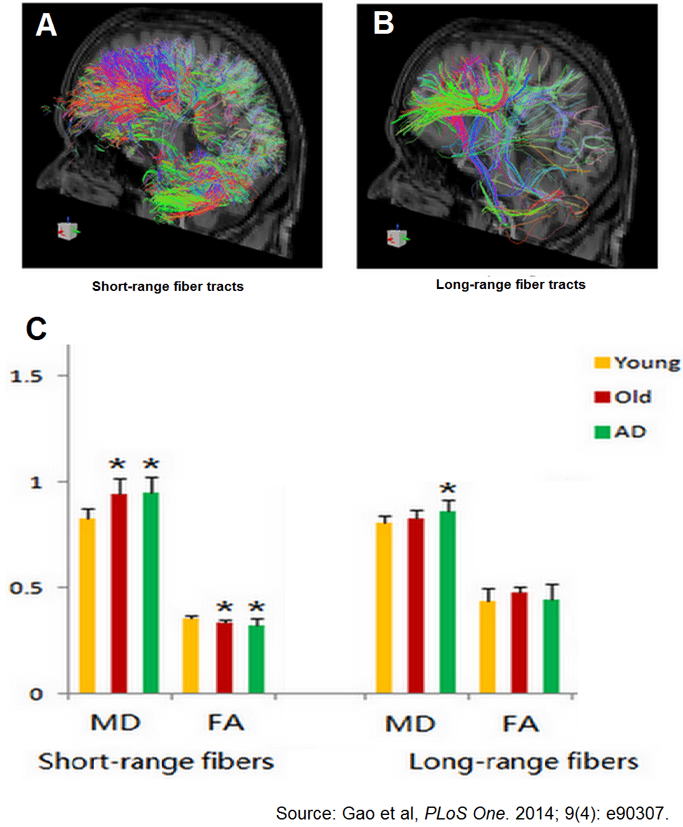
25. Gao J, Cheung RT, Chan YS, et al. The relevance of short-range fibers to cognitive efficiency and brain activation in aging and dementia. PLoS One. 2014; 9(4): e90307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090307
26. Acosta-Cabronero J, Alley S, Williams GB, Pengas G, Nestor PJ. Diffusion tensor metrics as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One. 2012; 7(11): e49072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049072
27. Clerx L, Visser PJ, Verhey F, Aalten P. New MRI markers for Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging and a comparison with medial temporal lobe measurements. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012; 29(2): 405-429. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110797
28. Wieshmann UC, Clark CA, Symms MR, et al. Reduced anisotropy of water diffusion in structural cerebral abnormalities demonstrated with diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999; 17(9): 1269-1274. doi: 10.1016/S0730-725X(99)00082-X
29. Eriksson SH, Stepney A, Symms MR, et al. Ultra-fast low-angle rapid acquisition and relaxation enhancement (UFLARE) in patients with epilepsy. Neuroradiology. 2001; 43(12): 1040-1045. doi: 10.1007/s002340100647
30. Rugg-Gunn FJ, Eriksson SH, Symms MR, Barker GJ, Duncan JS. Diffusion tensor imaging of cryptogenic and acquired partial epilepsies. Brain. 2001; 124(Pt 3): 627-636. doi: 10.1093/brain/124.3.627
31. Briellmann RS, Mitchell LA, Waites AB, et al. Correlation between language organization and diffusion tensor abnormalities in refractory partial epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2003; 44(12): 1541-1545. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2003.19403.x
32. Focke NK, Yogarajah M, Bonelli SB, et al. Voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis. Neuroimage. 2008; 40(2): 728-737. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.12.031
33. Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR in Biomedicine. 1995; 8(7-8): 333-344. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940080707
34. Basser PJ. New histological and physiological stains derived from diffusion-tensor MR images. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997; 820: 123-138. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb46192.x
35. Zhong J, Petroff OA, Prichard JW, Gore JC. Changes in water diffusion and relaxation properties of rat cerebrum during status epilepticus. Magn Reson Med. 1993; 30(2): 241-246. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910300214
36. Nakasu Y, Nakasu S, Kizuki H, et al. Changes in water diffusion of rat limbic system during status epilepticus elicited by kainate. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1995; 49(3): S228-S230. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1995.tb02184.x
37. Parekh MB, Carney PR, Sepulveda H, et al. Early MR diffusion and relaxation changes in the parahippocampal gyrus precede the onset of spontaneous seizures in an animal model of chronic limbic epilepsy. Exp Neurol. 2010; 224(1): 258-270. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.03.031
38. Moseley ME, Wendland MF, Kucharczyk J. Magnetic resonance imaging of diffusion and perfusion. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 1991; 3(3): 50-67.
39. Parmar H, Lim SH, Tan NC, Lim CC. Acute symptomatic seizures and hippocampus damage: DWI and MRS findings. Neurology. 2006; 66(11): 1732-1735. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000218207.18707.f4
40. Hugg JW, Butterworth EJ, Kuzniecky RI. Diffusion mapping applied to mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: preliminary observations. Neurology. 1999; 53(1): 173-176. doi: 10.1212/WNL.53.1.173
41. Assaf BA, Mohamed FB, Abou-Khaled KJ, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the hippocampal formation in temporal lobe epilepsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24(9): 1857-1862.
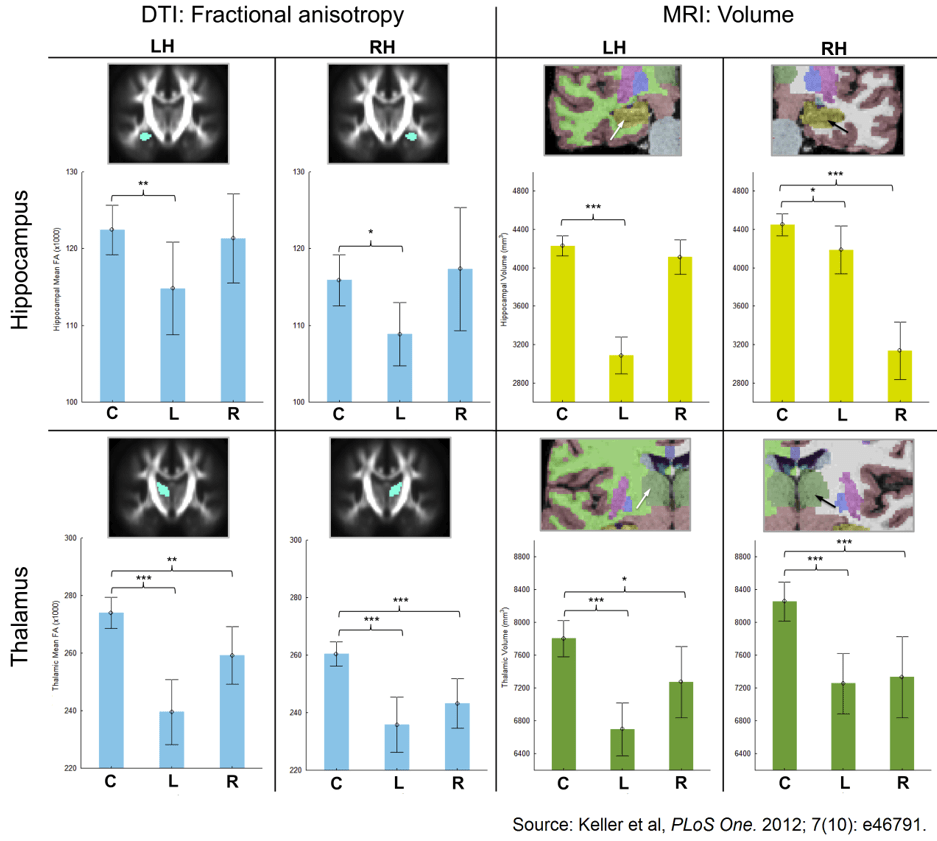
42. Keller SS, Schoene-Bake JC, Gerdes JS, Weber B, Deppe M. Concomitant fractional anisotropy and volumetric abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy: cross-sectional evidence for progressive neurologic injury. PLoS One. 2012; 7(10): e46791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046791
43. Gross DW, Concha L, Beaulieu C. Extratemporal white matter abnormalities in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy demonstrated with diffusion tensor imaging. Epilepsia. 2006; 47(8): 1360-1363. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00603.x
44. Arfanakis K, Hermann BP, Rogers BP, et al. Diffusion tensor MRI in temporal lobe epilepsy. Magn Reson Imaging. 2002; 20(7): 511-519. doi: 10.1016/S0730-725X(02)00509-X
45. Kim S, Pickup S, Hsu O, Poptani H. Diffusion tensor MRI in rat models of invasive and well-demarcated brain tumors. NMR Biomed. 2008; 21(3): 208-216. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1183
46. Concha L, Beaulieu C, Gross DW. Bilateral limbic diffusion abnormalities in unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 2005; 57(2): 188-196. doi: 10.1002/ana.20334
47. Concha L, Beaulieu C, Wheatley BM, Gross DW. Bilateral white matter diffusion changes persist after epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia. 2007; 48(5): 931-940. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01006
48. Richardson MP. Epilepsy and surgical mapping. Br Med Bull. 2003; 65: 179-192. doi: 10.1093/bmb/65.1.179
49. Zhang J, Liu W, Chen H, et al. Multimodal neuroimaging in presurgical evaluation of drug-resistant epilepsy. Neuroimage Clin. 2014; 4: 35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.10.017
50. Bhatia R, Bali P, Chaudhari RM. Epidemiology and genetic aspects of multiple sclerosis in India. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2015; 18(Suppl 1): S6-S10. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.164814
51. Shah P. Symptomatic management in multiple sclerosis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2015; 18(Suppl 1): S35-S42. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.164827
52. Meng X, Wang Q, Hou J, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of normal-appearing white matter in unilateral cerebral arterial occlusive disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 38(3): 650-654. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24004
53. Miller TR, Mohan S, Choudhri AF, Gandhi D, Jindal G. Advances in multiple sclerosis and its variants: conventional and newer imaging techniques. Radiol Clin North Am. 2014; 52(2): 321-336. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2013.11.011
54. Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, Di Chiro G. Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology. 1996; 201(3): 637-648. doi: 10.1148/radiology.201.3.8939209
55. Liu Y, Duan Y, He Y, et al. Whole brain white matter changes revealed by multiple diffusion metrics in multiple sclerosis: a TBSS study. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81(10): 2826-2832. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.11.022
56. Calabrese M, Rinaldi F, Seppi D, et al. Cortical diffusion-tensor imaging abnormalities in multiple sclerosis: a 3-year longitudinal study. Radiology. 2011; 261(3): 891-898. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11110195
57. Banaszek A, Bladowska J, Pokryszko-Dragan A, Podemski R, Sasiadek MJ. Evaluation of the degradation of the selected projectile, commissural and association white matter tracts within normal appearing white matter in patients with multiple sclerosis using diffusion tensor mr imaging-a preliminary study. Pol J Radiol. 2015; 80: 457-463. doi: 10.12659/PJR.894661
58. Commowick O, Fillard P, Clatz O, Warfield SK. Detection of DTI white matter abnormalities in multiple sclerosis patients. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008; 11(Pt 1): 975-982. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-85988-8_116
59. Faul M, Xu L, Wald MM, Coronado VG. Traumatic brain injury in the United States: emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths 2002-2006, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control: Atlanta (GA), 2010.
60. Inglese M, Makani S, Johnson G, et al. Diffuse axonal injury in mild traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103(2): 298-303. Available at: http://thejns.org/doi/abs/10.3171/jns.2005.103.2.0298?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&
61. Kraus MF, Susmaras T, Caughlin BP, et al. White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain. 2007; 130(Pt 10): 2508-2519. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm216
62. Geary EK, Kraus MF, Pliskin NH, Little DM. Verbal learning differences in chronic mild traumatic brain injury. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2010; 16(3): 506-516. doi: 10.1017/S135561771000010X
63. Rutgers DR, Fillard P, Paradot G, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging characteristics of the corpus callosum in mild, moderate, and severe traumatic brain injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29(9): 1730-1735. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1213
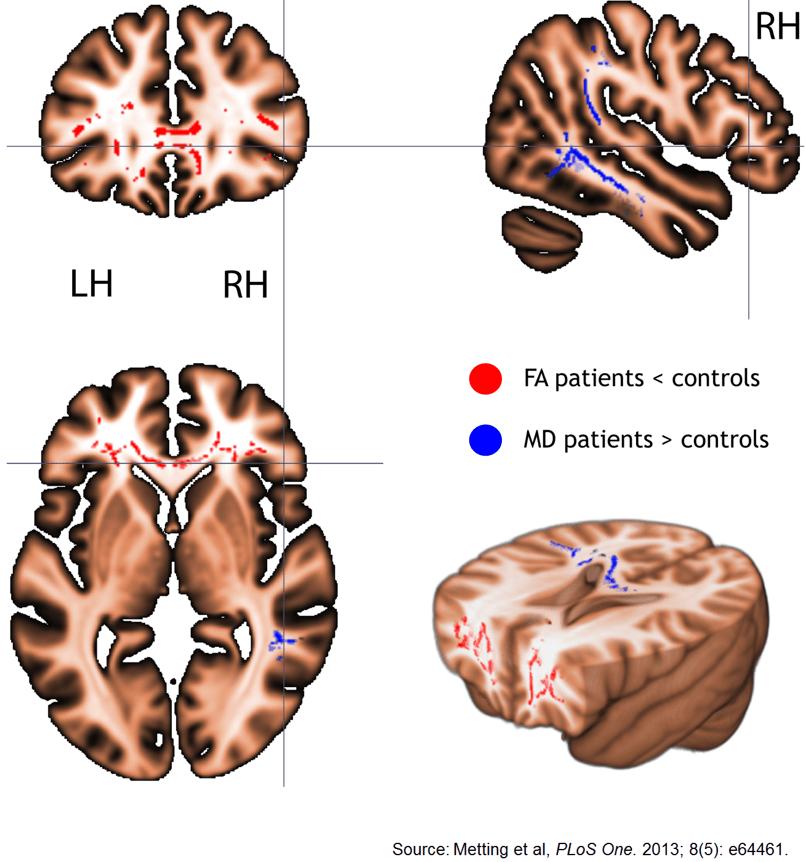
64. Metting Z, Cerliani L, Rodiger LA, Van Der Naalt J. Pathophysiological concepts in mild traumatic brain injury: diffusion tensor imaging related to acute perfusion CT imaging. PLoS One. 2013; 8(5): e64461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064461
65. Miles L, Grossman RI, Johnson G, et al. Short-term DTI predictors of cognitive dysfunction in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2008; 22(2): 115-122. doi: 10.1080/02699050801888816
66. Chen Z, Ni P, Zhang J, et al. Evaluating ischemic stroke with diffusion tensor imaging. Neurol Res. 2008; 30(7): 720-726. doi: 10.1179/174313208X297968
67. Mukherjee P. Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography in acute stroke. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2005; 15(3): 655-665, xii. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2005.08.010
68. Neil JJ. Diffusion imaging concepts for clinicians. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 27(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21087
69. Werring DJ, Toosy AT, Clark CA, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging can detect and quantify corticospinal tract degeneration after stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 69(2): 269-272. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.69.2.269
70. Ni J, Li ML, Yao M, Cui LY. Early corticospinal tract Wallerian degeneration on diffusion-weighted MR imaging after adult stroke: three cases report. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115(7): 1164-1166. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.09.027
71. Lukyanova LD, Kirova YI. Mitochondria-controlled signaling mechanisms of brain protection in hypoxia. Front Neurosci. 2015; 9: 320. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00320
72. Mariano G, Fink M, Hoffman C, Rosengart A. Intracranial pressure: monitoring and management in principles of critical care, McGraw-Hill Education LLC,: New York, NY, 2015: 1 online resource.
73. Ropper AH, Samuels MA, Klein J. Intracranial neoplasms and paraneoplastic disorders. In: Ropper AH, Samuels MA, Klein J, eds. Adams and Victor’s principles of neurology. McGraw Hill Medical,: New York, NY, 2014: 2v (xliii, 3,610, 158) .
74. Kubal WS. Updated imaging of traumatic brain injury. Radiol Clin North Am. 2012; 50(1): 15-41. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2011.08.010
75. Huisman TA. Diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor imaging of the brain, made easy. Cancer Imaging. 2010; 10(1A): S163-S171. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2010.9023
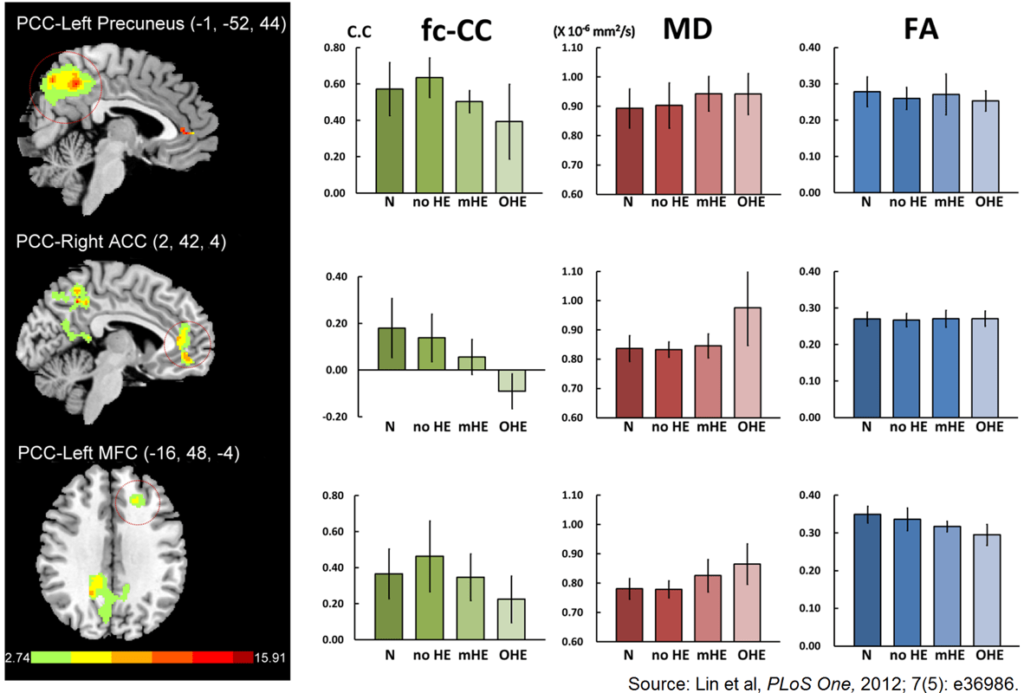
76. Lin WC, Hsu TW, Chen CL, et al. Connectivity of default-mode network is associated with cerebral edema in hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS One. 2012; 7(5): e36986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036986
77. Koch S, Rabinstein A, Falcone S, Forteza A. Diffusion-weighted imaging shows cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in eclampsia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22(6): 1068-1070. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.28.5.1082
78. Maegele M, Stuermer EK, Hoeffgen A, et al. Multimodal MR imaging of acute and subacute experimental traumatic brain injury: time course and correlation with cerebral energy metabolites. Acta Radiol Short Rep. 2015; 4(1): 2047981614555142. doi: 10.1177/2047981614555142
79. Suetomi Y, Kanchiku T, Nishijima S, et al. Application of diffusion tensor imaging for the diagnosis of segmental level of dysfunction in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spinal Cord. 2015. doi: 10.1038/sc.2015.192
80. Barakat N, Gorman MP, Benson L, Becerra L, Borsook D. Pain and spinal cord imaging measures in children with demyelinating disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2015; 9: 338-347. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.08.019
81. Lindberg PG, Sanchez K, Ozcan F, et al. Correlation of force control with regional spinal DTI in patients with cervical spondylosis without signs of spinal cord injury on conventional MRI. Eur Radiol. 2015. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3876-z
82. Chang ST, Xu J, Trinkaus K, et al. Optic nerve diffusion tensor imaging parameters and their correlation with optic disc topography and disease severity in adult glaucoma patients and controls. J Glaucoma. 2014; 23(8): 513-520. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e318294861d
83. Smith SA, Williams ZR, Ratchford JN, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the optic nerve in multiple sclerosis: association with retinal damage and visual disability. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32(9): 1662-1668. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2574