INTRODUCTION
Background
By violation of the underlying soft tissue which promotes contamination (and communication) with the external environment, open, compound fractures, are considered orthopedic emergencies. A break in the skin and exposure of underlying soft tissue leads directly to open communication with the open environment Subsequent treatment of gram-negative bacteria helps to reduce the bulk of infections.
The rate of injuries and open fracture has increased in the last few years. According to the literature, about 11.5 per 100,000 people in a year are facing an open fracture.1 Five percent (5%) of open fractures cases required specific and early treatment. Moreover, different complications are faced by the open fracture that includes bacterial infections, contractures, amputation, neuropathy, osteomyelitis, and loss of movement. The high-risk of infections is predicted in 60-70% of cases. The etiology for infection at the injured site are exposure to the fracture site, the weak immune system of the patient, introduction of a foreign body, dead tissue at the fracture site, and delayed treatment by late arrival to the hospital.1 The growth of microorganisms becomes favorable by the exposed subcutaneous tissue that provides a warm and favorable environment for the development of infection.2 These sites require immediate treatment; Surgical treatment with irrigation and debridement of dead tissue along with any foreign material is removed.3 Treatment of the open fracture is effective if treated within the first six-hours post injury. The aforementioned is known as the six-hour rule. Byrd and colleagues4 demonstrated that animals have shown a quick healing process when the debridement of the wound was performed within six-hours of injury. The open fracture threshold required by tissue to cause infection and was determined and elaborated that this achieved by the tissue within 5.17-hours of injury. Once the threshold is achieved, it is difficult to heal a wound and a severe infection is expected.5 Other than this, intravenous antibiotics can likewise be used along with the proper dressing. The bone or soft-tissue coverage can be used in which grafting of bone is done. The management of fracture site becomes difficult if an infection occurs as it results in delayed healing and an extensive treatment of the fracture.6 The main objectives for the management of open fracture include the bone union by preventing infection for the restoration of functions of bone.
Problem Statement
Despite the fact that the management of open fractures has been studied, a comparative study of pre-post-debridement cultures on the open fractures through meta-analysis has not been attempted.7 Accordingly, this research is conducted to understand the comparison of pre/post-debridement treatment in open fractures through meta-analysis to find out the effectiveness of both methods in the management of open fractures. Although, different studies have been completed in the past for the management of open fractures all those methods were for the determination of the effectiveness of different management techniques for open fractures.8 This paper will demonstrate the comparison of pre- and post-debridement cultures by using different indicators in addressing open fractures. Previously, different studies have been taken place for the management of open fractures but none of them deals with the effect of debridement timing on open fracture management through meta-analysis.9 This study aims to predict the infection rate according to time of culture, the effect of pre-debridement and post-debridement cultures on the open fracture and its effect on infection, thereby providing added insight in the attempt of healing the fracture and control of the infection. This study evaluates the study of comparative impact of pre-debridement and post-debridement cultures on open fractures.
Research Objectives
This study has different objectives to understand the efficiency of healing of fractures by pre-debridement and post-debridement surgeries. The following are the main objectives of the study.
1. Analysis of the effective treatments for the management of open fractures.
2. Analysis of the impact of pre/post-debridement culture in open fractures of the extremities through meta-analysis.
Practical Significance of the Study
The practical significance of this study is to help the surgeon regarding the debridement approach and to analyze the operative time of debridement for effective healing of the fracture. In brief, it will help to effectively deal with such orthopedic emergencies.
Open Fracture Management
Several studies have been done to investigate different approaches for the management of open fractures. These include irrigation and debridement, use of antibiotics, soft tissue and bone coverage, and stabilization of bone fragments.10 Therefore, the management within six hours of injury can lessen the chances of infection and help with healing. Thus, a study was undertaken to observe the effect of timing of injury on the infection rate and timing to close the open fracture. The patients of both genders with leg fractures were studied. Accordingly, it seems that there was no correlation between the infection and cause of fracture, the time of debridement after an injury, as well as gender or age.11 Besides, there was a stronger correlation of infection with pre-debridement culture than post-debridement culture. Finally, they concluded that there was better sensitivity for the detection of infections in pre-debridement cultures, while more specificity was present for post-debridement cultures.12
Relation Between Timing of Debridement and Infection Causing Microorganism
A recent study has shown the relation of infection rate with the timing of debridement and infection-causing microorganisms.13 Collectively, colleagues investigated a pilot project of comparison between the infection and bacterial flora. Besides, the pre-debridement wounds were obtained within the six hours of injury while post-debridement was obtained after 48-hours of injury during a follow-up period. The study recorded about 56% of patients who were contaminated with specifically coagulase-positive staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus during pre-debridement culture, while 44% of post-debridement patients developed an infection during the follow-up period. The medical condition and open fracture grade were not affected by post-operative infections. There were no infections by a similar organism in post-operative infections.13 But, the details of infectious microorganisms were not discussed in the study. A finding from Zhu et al14 determined that the effect of bacteria in open fractures infection was contaminated with seawater. The Gustilo-Anderson Type II and III open fracture patients with seawater contamination got a higher infection rate compared to others. Medications like ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin were effective for about 90% of pathogens. The treatment of open fractures contaminated with seawater was effective by cephalosporin with a quinolone.14 However, it has been demonstrated that the rate of infection Type II and III open fractures are higher compared to Type I.15
Relation of Infection Rate and Pre-Debridement Surgery
Different researchers have investigated the relation of infection rate and pre-debridement surgery of open fractures within sixhours after injury.16 Studies have detailed the infection pattern and effect of antibiotics in growing infections and infection-causing microorganisms in pre- and post-debridement surgeries. A study was prepared with 98 patients to observe the effect of infection time by pre- and post-debridement surgeries. The follow-up of 14-days was maintained for post-debridement surgery. The results showed that about fifty-two samples of pre-debridement treatment showed infections by Staphylococcus aureus. The infection rate was 58.9% after the 14-days follow-up.16 However, there were no similar organisms that were causing the infections in pre- and post-debridement surgeries.
Relation of Infection Rate and Post-Debridement Surgery
In the past, different studies have been conducted for determining the effect of infection rate on the post-debridement culture of open fractures. The study by Hull et al17 demonstrated the relationship of post-debridement culture and infection rate in different patients having open fractures. The mean time interval of post-debridement treatment for fracture was about 10.6-hours. The deep infections found were about 10%. Fifty five patients (Gustilo-Anderson Grade I) with open fractures showed no infection after delay but after each delayed hour, there was an increase in deep infection rate for grade II and III injuries.
The increase in infection rates concerning time showed a linear relationship. The bacterial contamination in open fractures was the main reason for deep infection. The post-debridement culture has a more adverse effect on the open fracture as compared to the pre-debridement culture. Delayed treatment is only effective when grade I infection occurs while contamination, higher grade of fractures and other negative factors move towards the debridement surgery.17 However, in this study, exact time after which the infection starts is not identified.
Relation of Pre- and Post-Debridement with the Infection Rate
The investigation of the impact of debridement in the treatment of open bone and infection rate was studied by different researchers.18 The frequency of culture, its time, and the organism that infected the fracture injury were necessary to predict a suitable antibiotic treatment for patients. A prospective study was done to study the different samples. During the pre-debridement period, significant growth was observed for 15% culture and the isolated species that was about 53% of the total was Staphylococcus aureus while about 41% cultures showed a specific growth during debridement period. It was estimated that about 53% pre-debridement patients and 66% of debridement patients developed post-operative infections. About 39% of patients showed positive cultures that confirmed the presence of post-operative infections. The pre-debridement and debridement cultures revealed a sensitivity of 21% and 69% respectively. The higher sensitivity in debridement culture showed high antimicrobial therapy.18 The comparison of the efficacy of pre-debridement and post-debridement cultures in open fractures was completed.19 The results obtained by this comparison were based on the infection causing microorganism and the subsequent infection rate. The results indicated the sensitivity and specificity of 70% and 55% respectively in post-debridement culture while pre-debridement showed specificity and sensitivity of 24% and 64% respectively.19 The post-debridement cultures have the most chances of infection as compare to pre-debridement as shown in results gleaned by Nusbaum et al.20 This study investigates the efficiency comparison but does not explain the reason why post-debridement culture showed more chances of infection as compared to pre-debridement culture on open fractures. According to Bhatty et al,21 they evaluated the efficiency and role of microorganisms in bacterial cultures on the fractured site. The pre- and post-debridement and intra-operative wounds were collected and observed for detecting the infecting microorganisms. The infections caused at the initial stages were by the Gram-negative microorganisms while Gram-positive microorganisms were responsible for infections in delayed wounds. No infection was caused in pre-debridement cultures. Several negative cultures revealed infections. It was concluded the growth of microorganisms moved from negative to positive after the second week. This showed that the initial dressing or treatment within the first 24-hours is not an indicator for determining the infection in the pre- and post-debridement cultures,21 and the study does not determine the actual indicators for causing infections.
Systematic Review of Infection Rate and Time of Debridement in Open Fractures
The systematic review of debridement of open fractures was done through meta-analysis to determine the time to debridement and infection rate. The evaluation was done by random trials and the quantitative data was obtained through meta-analysis. The results presented that no difference was observed in the infection rate by pre-debridement or post-debridement culture on open fractures. According to the pieces of evidence obtained, infection depth and the Gustilo-Anderson classification, there was no difference in infection rate with early or late debridement. The six-hour rule treatment exhibited little significance in the literature and the infection rate and delayed debridement have no association between them.1 However, additional studies are required to study the effect of delayed debridement or post-debridement on the infection rate.
Ibrahim et al22 performed a systematic review of the literature by comparing the infection rate of pre-debridement and post-debridement culture in an open fracture. A meta-analysis was done by using random models to analyze the effect of infection in children with early debridement and late debridement. It was concluded in this study that there was no link between the infection rate and post-debridement treatment. Similar results were obtained by the pre- and post-debridement cultures. However, pre-debridement treatment was effective for children to prevent them from a high-risk of infections. As the pre-debridement treatment helped in early healing of injury.22 The systematic review performed by Ketonis et al23 determined the rate of debridement time on infection and the effectiveness of antibiotics in the management of open fractures. The quantitative analysis was done and the comparison of the effect of treatment and infection rate was performed through meta-analysis. Different references were used including 12 articles showing 4.6% infectious patients out of total cases. It was shown that a 4.2% infection rate was observed with pre-debridement culture according to six-hours’ rule while a 3.6% infection rate was observed with a post-debridement culture of 12-hours. Some studies did not indicate any relation between infection rate and debridement timing.23 It was concluded that somehow, antibiotics can be used to treat the infections. The timing of debridement did not change the rate of infection but the rationale for this finding was not well explained in this study.
METHODOLOGY
Setting
The relevant data of the open fracture was collected from the comprehensive research of online sources, including Cochrane, Medline, Google Scholar, Excerpta medica dataBASE (EMBASE), computerized literature database, PubMed, and Scopus. The data collected was based on different types of studies, including prospective and retrospective. A prospective study included the study of some specific object over a certain period and determining the factors affecting the object while a retrospective study involves the history and background of the targeted object and its influence on the present study. Furthermore, the review articles that were missed by the electronic search were searched by the citations of different articles. The terms used for the search of data were-debridement, open fracture, management of open fractures, pre-debridement, post-debridement, bacterial culture, upper extremities, lower extremities, and infection rate.
Patients
The patients in this research present a wide variety of open fracture in different extremities, both genders, and classification of fracture, Chronic wounds such as venous or diabetic foot ulcers were excluded in this study bones.
The inclusive criteria include (1) open fractures of different extremities (2) infection rates (3) timing of debridement (4) patients of both genders and of any age (5) staged healing of wounds, (6) microorganisms that generated an infection, and (7) classification of open fractures. Exclusive criteria was identified: (1) research work not meeting the research criteria (2) having closed fracture, (3) orthopedic care on animals (4) gunshot injuries or (5) having short bones (toes, fingers, thumbs).
Data Extraction
The data for the study was extracted from different articles, review papers and research reports. The extracted data consists of the general information of the article including the type of study, year of publication, gender, and age of the patient, as well as the duration of patient admittance, infection rate, classification of an open fracture, and the management strategy for an open fracture.
The quality of information was assessed by analyzing including a sampling, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Data Synthesis
A meta-analysis was done by relating the individual effect of pre-debridement/post-debridement on the management of open fracture and its comparison for investigating its efficiency over one another. The infection rate along with the debridement treatment was observed for open fractures. The analysis was done at different time intervals. The data was collected by the relationship between the effects of the infection rate on debridement.
RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
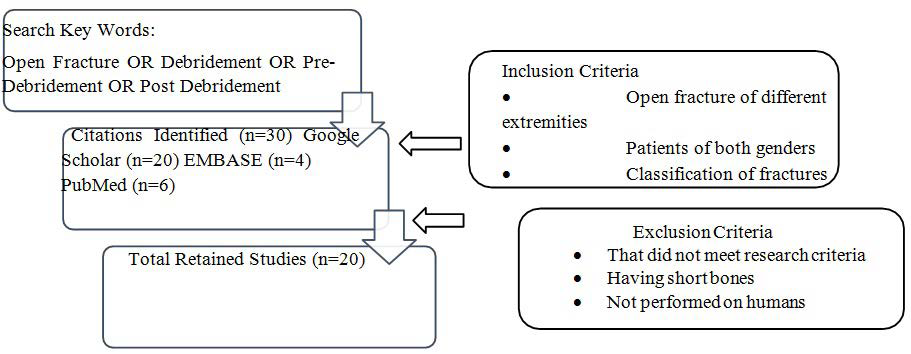
The initial results were obtained by different citations from Google Scholar, PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, Medical literature analysis and retrieval system online (MEDLINE), and Cochrane. The systematic review of the literature identified 118 relevant articles. After excluding duplicate publications, 20 studies retained and were subjected to a preliminary screening (Figure 1). Only those articles in which the citations followed our research criteria were selected for inclusion in this study. This systematic review includes articles based on open fracture management and comparison of pre-debridement and posts-debridement cultures However, the comparison was based on the threshold of the timing of debridement to investigate its effects on the infection rate of pre-debridement and post-debridement culture. The minimum timing to investigate the debridement was six-hours post injury (six-hour rule). The effect of antibiotics in the debridement culture there has been identified. Different studies in the literature include the effect of antibiotics in the debridement of open fractures. Different respond differently to antibiotics, thus changing the infection rate. The antibiotics include ampicillin, penicillin, cefazolin, cefuroxime, and flucloxacillin. About five studies demonstrated the use of antibiotics for treating infections. The different antibiotics used in different studies for determining its effect on infection rates are given in Table 1. However, there is the effect of timing of debridement along with antibiotics on the infection rate. In the past, different studies have been carried out to investigate the effect of timing of debridement on infection rate. Similarly, different studies have explained the effect of the antibiotic on the infection rate.24 Table 1 demonstrates the different studies by linking the relation of antibiotics along with the timing of debridement on the infection rate. The use of Ancef I as an antibiotic during the starting hours of fracture helps in reducing the chances of infection, thus showing only 1.4% of infection in patients. Similarly, the increase in time to treatment of open fracture and post-debridement surgery can increase the chances of infection rate if the antibiotic is not used with it.
Figure 1. Depiction of the Data Selection for Systematic Review
| Table 1. Relation between Infection Rate and Timing of Debridement |
|
Author
|
Year |
Antibiotic Used |
Timing to Debridement |
Infection Rate (%) |
References
|
|
Pre- Debridement
|
Post-Debridement
|
| Ng et al |
2012
|
Cephazolin |
|
23-hours |
11.4% |
25
|
| Capo et al |
2011
|
Ancef I |
Within 6-hours |
|
1.4% |
26
|
| Bannasch et al |
2010
|
Cefuroxime |
Within 8-hours |
|
2.91% |
27
|
| Komorcu li et al |
2008
|
Penicillin |
|
24-hours |
8.69% |
28
|
| Steverson et al |
2003
|
Flucloaclin |
Within 12-hours |
|
3.62% |
29
|
| Almeida et al |
2013
|
Not reported |
|
26-hours |
28% |
30
|
| Pollack et a |
2010
|
Not reported |
Within 10-hours |
|
27% |
31
|
| Mclain et al |
1991
|
Not reported |
Within 7-hours |
|
11.11% |
32
|
Effect of Threshold Debridement Timing on Infection Rate
As most of the data supports the importance of the six-hour rule, different studies were conducted for determining the infection rate by considering the six-hours of injury as threshold timing, a minimum time required by tissue to respond to contamination.33 For this, different studies are compared through meta-analysis for determining the effect of threshold timing on the infection rates of pre-debridement and post-debridement surgery.
Naique et al34 considered the six-hour rule and fixed the threshold timing to 6-hours and investigated the effect on the infection rate. It was found that only 7.1% of patients were found to be infected if treated by the pre-debridement surgery but the infection rate was 16% in post-debridement cultures. Similarly, the infection rate was determined35 by finding the relationship between threshold timing and debridement of open fractures. The infection rate was 3% in pre-debridement culture while a 2% infection rate was found in post-debridement culture. The lesser rate of infection in post-debridement culture shows the effect of some other factors that were not investigated in this study. The summarization regarding the relationship between the rate of infection and the time to debridement is given in Table 2. Moreover, different studies that followed the six-hour rule found that the pre-debridement infection rate was less as compared to post-debridement except in a few cases. Lower infection rates in post-debridement seem to have an effect of selecting out microorganisms that were causing infections.
| Table 2. Relation between Infection Rate and Time Threshold to Debridement |
|
Author
|
Year |
Time Thresh Old to Debridement |
Infection Rate (%) |
References
|
|
Pre- Debridement
|
Post-Debridement
|
| Naique et al |
2006
|
6-hours |
7.1 |
16 |
34
|
| Skaggs et al |
2005
|
6-hours |
3 |
2 |
35
|
| Spencer et al |
2004
|
6-hours |
10.1 |
10.8 |
36
|
| Khatood et al |
2003
|
6-hours |
16 |
20 |
37
|
| Harley et al |
2002
|
6-hours |
8 |
7 |
38
|
| Skaggs et al |
2000
|
6-hours |
2.5 |
6 |
39
|
| Kindsfater et al |
1995
|
6-hours |
7 |
35 |
40
|
| Parikh et al |
1993
|
6-hours |
9 |
3.4 |
41
|
Determination of Isolates of Microorganisms from Pre- and
Post-debridement Cultures
As the bacterial infection has undesirable results, so it is required to lessen the chances of bacterial infection by taking different measurements. For this, diagnosis is most important before treatment so proper steps can be initiated. Different studies have demonstrated that bacterial cultures affect the pre-debridement and post-debridement treatment of open fractures (Table 3). All these studies were taken at different years and different bacteria were isolated from the infection site. It was discovered that different bacteria were responsible for pre-debridement and post-debridement infection. In most cases, the gram-negative bacteria were responsible for pre-debridement infection while gram-positive bacteria were responsible for post-debridement infection.
| Table 3. Number of Isolates of Microorganisms from Pre-Debridement and Post-Debridement Culture |
|
Author
|
Year |
Bacteria |
No. of isolates |
References
|
|
Pre- Debridement
|
Post-Debridement
|
| Adisesh Mangala et al |
2018
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
14 |
9 |
18
|
| Shiraz Bhatty et al |
2018
|
Acinitobacter |
20 |
1 |
21
|
| Fred Chuma et al |
2017
|
Klebsilla |
15 |
12 |
16
|
| D’Souza et al |
2008 |
Pseudomonas |
7 |
5 |
12 |
It was studied18 that the isolated microorganism from the fractured site was Staphylococcus aureus which showed the isolation of 14 and 9 from pre-debridement and posts debridement culture. Similar studies were undertaken place by different researchers in different years to determine the infection-causing organism. Different microorganisms respond differently to the fractured site and their growth rate depends on different factors.
DISCUSSION
This research paper represents the analysis of different studies on the treatment of open fracture through meta-analysis. Therefore, we noted no direct relationship between infection rate and debridement culture. Thus, the comparison of pre- and post-debridement on open fracture was made, and it was found that post-debridement has more adverse infection rates compared to pre-debridement if no antibiotic is used. In our study, data was extracted from the available literature regarding debridement timing and the antibiotic effect on the infection rate. Besides, the study includes fracture types, age, gender of patients, and the number of fractures. As we know, the management of open fracture needs various treatments. Debridement continues to be the primary and essential step for the prevention of infection from the fractured site. Once an infection starts, it is challenging to heal a wound by treating the infection. Various studies investigated the pre-debridement and post-debridement effect on open fractures.
Accordingly, antibiotic therapy helps to treat infections, but different antibiotics work in a different way to lessen the infection rate. For this, eight studies of different researchers were investigated to find the relation of debridement on infection rate. It was singularly relevant that although the debridement timing effects the infection rate, antibiotics directly affect the infection rate along with debridement timing.29 The use of flucloxacillin within twelve-hours of injury revealed an infection rate of 3.62%.
Eight research studies investigated the impact of threshold debridement as determined on the pre-debridement and post-debridement infection rates. Six out of eight studies further investigated the correlation of threshold timing of debridement on the infection rate. Different pre-debridement and post-debridement infection rates were observed at the threshold timing of six-hours. The results displayed that although the threshold timing might be the same there was a distinct difference in pre- and post-debridement infection rates and alluded to the fact that there was an underlying inter-dependence of other intervening factors.
CONCLUSION
The systematic review through meta-analysis concludes the study that although the timing of debridement and antibiotic effects of the infection rate, different factors also contribute to promoting or lessening infection rates. Pre-debridement culture has lesser effect on the infection rate then the post-debridement culture. Although infection-causing microorganism responds differently to pre- and post-debridement cultures. However, early treatment with debridement for open fractures has a more positive effect on superficial, less bulky infections as well as contributing to early vigor and stabilization of the wound.
Implications of Our Review
Although, management of open fracture by irrigation and debridement should be the main concern, early debridement is not possible in some situations. In remote areas, there are no proper facilities to treat such injuries so it may result in post-debridement treatment rather than early. The movement of a patient from a remote area to a nearby hospital with full facilities may result in late surgery that can have different consequences. Moreover, as these open fractures are considered as orthopedic emergencies, these emergencies should be treated with proper facilities and management in hospitals but improper treatment results in severe consequences.
In our review, different indicators are compared to find the relation of debridement timing and antibiotic with infection rate. Moreover, the effect of microorganisms has also been studied on pre-debridement and post-debridement infection rates. So, the findings of this review can be used to diagnose the causes of infections as well as the effective time before which treatment can be undertaken to prevent infections and to promote effective healing. The need for further studies relevant to this orthopedic emergency is important as a delay in the treatment of open fractures results in severe consequences. This review, in advocating certain protocols (adjusting the time to intervention and the extent of antibiotic treatment) can help in delineating policy guidelines and can advocate treatment protocols, that promote a successful management for open fractures.
Future Directions
Although our study provides sufficient information regarding the pre-debridement and posts debridement analysis, there is still room to investigate different factors that are affecting the debridement culture on open fractures. Further investigations can be studied with regards to the timing of debridement as it relates to the infection if the bacterial growth is controlled. Moreover, the six-hour rule should always be considered to evaluate a threshold time for debridement.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.






