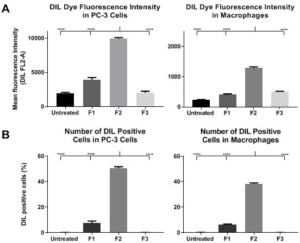
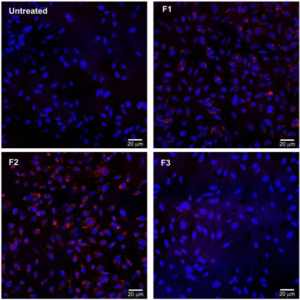
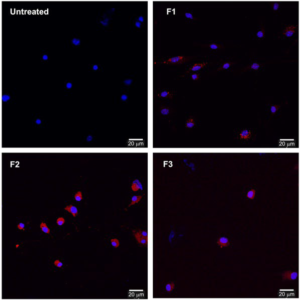
1. Bozzuto, G, Molinari, A Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015; 10: 975-999. doi: 10.2147/Ijn.S68861
2. Bangham A. The 1st description of liposomes – a citation classic commentary on Diffusion of Univalent Ions across the Lamellae of Swollen Phospholipids by Bangham AD, Standish MM, Watkins JC. Current Contents/Life Sciences. 1989(13): 14. Website. http:// garfield.library.upenn.edu/classics1989/A1989T670000001.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2020.
3. Azadi A, Ashrafi H. Cell organelle-shaped liposomes: A novel approach to present the stable intracellular drug delivery systems. Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016; 2(2): 85-88.
4. Torchilin VP. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2005; 4(2): 145-160. doi: 10.1038/nrd1632
5. Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y, et al. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013; 8(1): 102. doi: 10.1186/1556- 276X-8-102
6. Çağdaş M, Sezer AD, Bucak S. Liposomes as potential drug carrier systems for drug delivery. In: Application of Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery. 2014. doi: 10.5772/58459
7. Allen TM, Cullis PR. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2013; 65(1): 36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.037
8. Li J, Wang, XL, Zhang, T, Wang C, Huang Z, Luo X, et al. A review on phospholipids and their main applications in drug delivery systems. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2015; 10(2): 81-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2014.09.004
9. Lian, T, Ho, RJ Trends and developments in liposome drug delivery systems. J Pharm Sci. 2001; 90(6): 667-680. doi: 10.1002/ jps.1023
10. Sofou, S, Sgouros, G Antibody-targeted liposomes in cancer therapy and imaging. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008; 5(2): 189-204. doi: 10.1517/17425247.5.2.189
11. Sawant, RM, Hurley, JP, Salmaso, S, Kale A, Tolcheva E, Levchenko TS, et al. “SMART” drug delivery systems: Double-targeted pH-responsive pharmaceutical nanocarriers. Bioconjug Chem. 2006; 17(4): 943-949. doi: 10.1021/bc060080h
12. Pasut, G, Paolino, D, Celia, C, Mero A, Joseph AS, Wolfram J, et al. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-dendron phospholipids as innovative constructs for the preparation of super stealth liposomes for anticancer therapy. J Control Release. 2015; 199: 106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.008
13. Pasut G, Veronese FM. State of the art in PEGylation: the great versatility achieved after forty years of research. J Control Release 2012; 161(2): 461-472. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.10.037
14. Harris JM, Chess RB. Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003; 2(3): 214-221. doi: 10.1038/nrd1033
15. Magarkar A, Dhawan V, Kallinteri, P, Viitala T, Elmowafy M, Róg T, et al. Cholesterol level affects surface charge of lipid membranes in saline solution. Sci Rep. 2014; 4: 5005. doi: 10.1038/ srep05005
16. Yan X, Scherphof GL, Kamps JA. Liposome opsonization. J Liposome Res. 2005; 15(1-2): 109-139. doi: 10.1081/lpr-64971
17. Henao-Tamayo, M, Shanley, CA, Verma, D, Zilavy A, Stapleton MC, Furney SK, et al. The efficacy of the BCG vaccine against newly emerging clinical strains of mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2015; 10(9): e0136500. doi: 10.1371/journal. pone.0136500
18. Tameris, MD, Hatherill, M, Landry, BS, Scriba TJ, Snowden MA, Lockhart S, et al. Safety and efficacy of MVA85A, a new tuberculosis vaccine, in infants previously vaccinated with BCG: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2013; 381(9871): 1021-1028. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60177-4
19. Piccolo, M, Misso, G, Ferraro, MG, Riccardi H, Capuozzo A, Zarone MR, et al. Exploring cellular uptake, accumulation and mechanism of action of a cationic Ru-based nanosystem in human preclinical models of breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1): 7006. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43411-3
20. Skwarczynski M, Hayashi Y, Kiso Y. Paclitaxel prodrugs: Toward smarter delivery of anticancer agents. J Med Chem. 2006; 49(25): 7253-7269. doi: 10.1021/jm0602155
21. Litwin MS, Tan HJ. The diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer: A review. JAMA. 2017; 317(24): 2532-2542. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7248
22. Hema S, Thambiraj S, Shankaran DR. Nanoformulations for targeted drug delivery to prostate cancer: An overview. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018; 18(8): 5171-5191. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2018.15420
23. Serradell, MC, Rupil, LL, Martino, RA, Prucca CG, Carranza PG, Saura, A et al. Efficient oral vaccination by bioengineering virus-like particles with protozoan surface proteins. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1): 361. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08265-9
24. Samad A, Sultana Y, Aqil M. Liposomal drug delivery systems: an update review. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007; 4(4): 297-305. doi: 10.2174/156720107782151269
25. Kaighn, ME, Narayan, KS, Ohnuki, Y, Lechner JF, Jones LW. Establishment and characterization of a human prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC-3). Invest Urol. 1979; 17(1): 16-23.
26. Skwarczynski M, Toth I. Peptide-based synthetic vaccines. Chem Sci. 2016; 7(2): 842-854. doi: 10.1039/c5sc03892h
27. Skwarczynski, M, Zhao, GZ, Boer, JC, Ozberk V, Azuar A, Cruz JG, et al. Poly(amino acids) as a potent self-adjuvanting delivery system for peptide-based nanovaccines. Sci Adv. 2020; 6(5): eaax2285. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax2285
28. Thakur A, Mikkelsen H, Jungersen GIntracellular pathogens: Host immunity and microbial persistence strategies. J Immunol Res. 2019; 2019: 1356540. doi: 10.1155/2019/1356540
29. Al-Attiyah R, El-Shazly A, Mustafa AS. Comparative analysis of spontaneous and mycobacterial antigen-induced secretion of Th1, Th2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of tuberculosis patients. Scand J Immunol. 2012; 75(6): 623-632. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2012.02692.x
30. Umeshappa, CS, Xie, Y, Xu, S, Nanjundappa RH, Freywald A, Deng Y, et al. Th cells promote CTL survival and memory via acquired pMHC-I and endogenous IL-2 and CD40L signaling and by modulating apoptosis-controlling pathways. PLoS One. 2013; 8(6): e64787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064787
31. Olusanya, TOB, Haj Ahmad, RR, Ibegbu, DM, Smith JR, Elkordy AA. Liposomal drug delivery systems and anticancer drugs. Molecules. 2018; 23(4): 907. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040907
32. Kroon, J, Metselaar, JM, Storm, G, van der Pluijm G. Liposomal nanomedicines in the treatment of prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014; 40(4): 578-584. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.10.005
33. Zhang, W, Song, Y, Eldi, P, Guo X, Hayball JD, Garg S, et al. Targeting prostate cancer cells with hybrid elastin-like polypeptide/liposome nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018; 13: 293-305. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S152485
34. Khademi, F, Taheri, RA, Momtazi-Borojeni, AA, Farnoosh G, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A. Potential of cationic liposomes as adjuvants/delivery systems for tuberculosis subunit vaccines. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2018; 175: 47-69. doi: 10.1007/112_2018_9
35. Marasini N, Ghaffar KA, Skwarczynski M, Toth I. Liposomes as a vaccine delivery system. In: Micro and Nanotechnology in Vaccine Development. Norwich, NY, USA: William Andrew Inc; 2017: 221- 239. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-39981-4.00012-9
36. Ghaffar KA, Marasini N, Giddam AK, Batzloff MR, Good MF, Skwarczynski M, et al. Liposome-based intranasal delivery of lipopeptide vaccine candidates against group A streptococcus. Acta Biomater. 2016; 41: 161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.04.012
37. Ghaffar, KA, Giddam, AK, Zaman, M, Skwarczynski M, Toth I. Liposomes as nanovaccine delivery systems. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 2014; 14(9): 1194-1208. doi: 10.2174/1568026614 666140329232757
38. Zhang M, Desai T, Ferrari M. Proteins and cells on PEG immobilized silicon surfaces. Biomaterials. 1998; 19(10): 953-60. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00026-x
39. Wischerhoff, E, Uhlig, K, Lankenau, A, Börner HG, Laschewsky A, Duschl C, et al. Controlled cell adhesion on PEG-based switchable surfaces. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008; 47(30): 5666- 568. doi: 10.1002/anie.200801202
40. Immordino, ML, Dosio, F, Cattel, L Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006; 1(3): 297-315.
41. Sanchez L, Yi Y, Yu Y. Effect of partial PEGylation on particle uptake by macrophages. Nanoscale. 2017; 9(1): 288-297. doi: 10.1039/c6nr07353k
42. Takano S, Aramaki Y, Tsuchiya S. Physicochemical properties of liposomes affecting apoptosis induced by cationic liposomes in macrophages. Pharm Res. 2003; 20(7): 962-968. doi: 10.1023/a:1024441702398
43. Epstein-Barash H, Gutman D, Markovsky E, Mishan-Eisenberg G, Koroukhov N, Szebeni J, et al. Physicochemical parameters affecting liposomal bisphosphonates bioactivity for restenosis therapy: Internalization, cell inhibition, activation of cytokines and complement, and mechanism of cell death. J Control Release. 2010; 146(2): 182-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.03.011
44. Straubinger, RM, Hong, K, Friend, DS, Papahadjopoulos D. Endocytosis of liposomes and intracellular fate of encapsulated molecules: Encounter with a low pH compartment after internalization in coated vesicles. Cell. 1983; 32(4): 1069-1079. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90291-x
45. Muller, WJ, Zen, K, Fisher, AB, Shuman H. Pathways for uptake of fluorescently labeled liposomes by alveolar type II cells in culture. Am J Physiol. 1995; 269(1 Pt 1): L11-L19. doi: 10.1152/ ajplung.1995.269.1.L11
46. Poelma, DL, Ju, MR, Bakker, SC, Zimmermann LJ, Lachmann BF, van Iwaarden JF. A common pathway for the uptake of surfactant lipids by alveolar cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004; 30(5): 751-758. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0127OC
47. Quintero OA, Wright JR. Metabolism of phosphatidylglycerol by alveolar macrophages in vitro. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000; 279(2): L399-L407. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2000.279.2.L399