INTRODUCTION
Tibial plateau fractures account for 1-2% of all fractures and are caused by a valgus or varus force and axial loading at the knee.1 The varying direction and magnitude of forces applied and pre-existing quality of patient’s bones results in a wide spectrum of fracture patterns.2 Hohl et al3 reported that 55-70% of tibial plateau fractures involve the lateral plateau and about 7% involve the posterolateral tibial plateau.
Tibial plateau fractures are classified by either the more complex and precise Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen/Orthopaedic Trauma Association (AO/OTA) system or the more reproducible and reliable Schatzker method.4,5,6 For the AO/OTA system, the proximal tibia is coded as a 41 with further subgroupings based on intra-articular fractures with B1-3 for partial and C1-3 for complete involvement.6 The Schatzker method divides tibial plateau fractures into 6 types: 1) split fracture of the lateral plateau; 2) split depression of the lateral plateau; 3) central depression of the lateral plateau; 4) split of the medial tibial plateau; 5) bicondylar tibial plateau fracture OR; 6) tibial plateau fracture with dissociation between the metaphysis and diaphysis.6
Surgical management is indicated if articular step-off is greater than 3 mm, condylar widening is greater than 5 mm, there is greater than 5° of coronal alignment disruption, or there is instability to varus and valgus stress of the knee joint with the leg in extension.7
This report describes a unique injury pattern of a right unicondylar lateral plateau fracture with dislocation and subsequent relocation of the fibular head, resulting in a large shear fragment of the plateau behind the spontaneously relocated fibular head, with entrapment of an intact peroneal nerve.
CASE REPORT
The patient is a 38-year-old female with a past medical history significant for IV drug use, cocaine use, hepatitis C, bipolar disorder, anxiety and depression who presented post high-energy motor vehicle accident (MVA) accident, sustaining many injuries. She was an unrestrained driver driving 100 mph, drove through a ditch, and was launched into the woods 30-40 feet into a tree. It is unknown if she lost consciousness or if she was intoxicated while driving. She was brought by ambulance to an outside hospital, where imaging was done on bilateral lower extremities, her bilateral ankles reduced and splinted and then transferred to an academic level one trauma hospital for further care. A healthcare proxy was unable to be discerned as her immediate family had all passed away, she was estranged from her extended family, and the patient was unable to verify if she had a spouse.
On physical examination, she appeared intoxicated with slurred speech and lethargy with waxing and waning arousability. All her injuries were closed. She refused to cooperate with the motor examination but no foot drop observed. Bilateral lower extremities had sensation intact to light touch. There was an obvious valgus deformity of the right knee with gross instability to valgus stress testing, intact to varus stress testing. She had bilateral ankle swelling and deformities but intact distal pulses, motor, and sensation. Her dorsalis pedis pulses were not palpable but were dopperable bilaterally. Her toes were warm and well-perfused.
Right leg X-rays (Figure 1) showed a comminuted lateral tibial plateau fracture, and fractures of the medial and lateral malleoli. Computerized tomography (CT) further, elucidating that the lateral tibial plateau fracture has posterior displacement and angulation of the tibial articular surface fracture fragment which abutted the popliteal neurovascular bundle (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Plain Radiographs Demonstrating Comminuted
Lateral Tibial Plateau Fracture in A) AP and B) Lateral Views
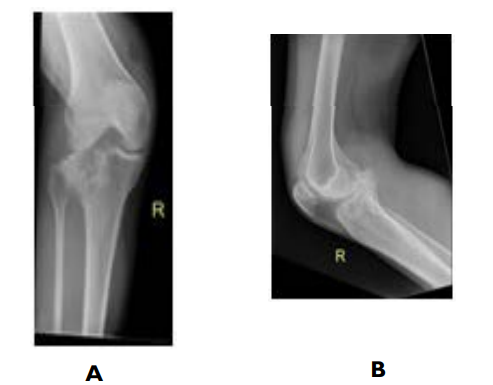
Figure 2. A. Axial, B. Sagittal, C. Coronal
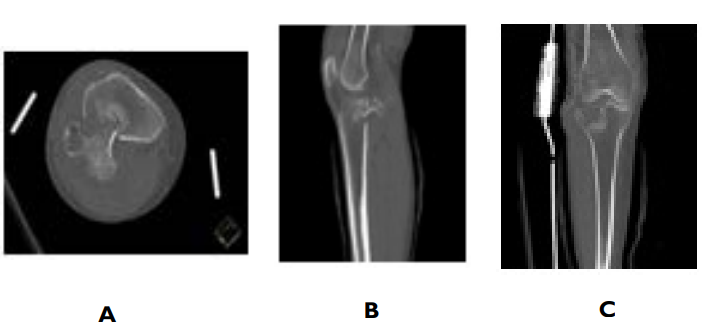
Computerized tomography views demonstrating lateral tibial plateau fracture with posterior displacement and angulation of the tibial articular surface fracture fragment, abutting the popliteal neurovascular bundle.
In the emergency department (ED), the orthopedic team placed right tibia in a splint. Due to her young age and unique fracture pattern of her right lateral tibial plateau, her treatment plan was surgery. However, two days after admission, the psychiatry team placed her on a Section 12 and stated that she lacked capacity to consent to surgery. She was closely monitored in the hospital and four days after admission was able to go to the operating room.
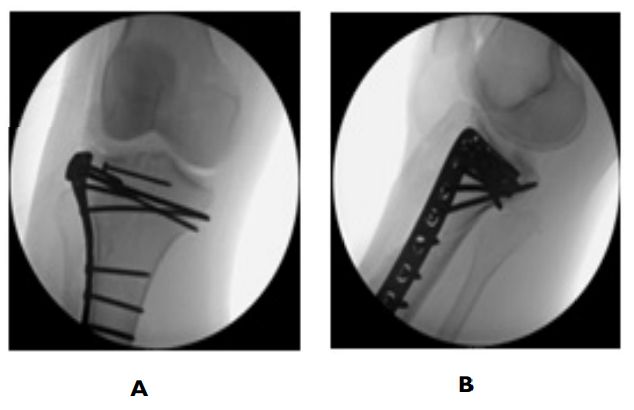
She was taken to the OR and under general anesthesia, her ankle and foot fractures were treated operatively, as well as her tibial plateau. To fix the tibial plateau, an incision was made anterior laterally. A laminar spreader was used to open the anterior fracture site to bring the fibular head and the intact common peroneal nerve in view. The nerve was behind the fibular head, displaced into the fracture plane. The large posterior lateral shear fragment of the tibial plateau was behind the fibular head. A laminar spreader and femoral distractor were used to dislocate the fibular head and obtain length. Then, a large kidney clamp was placed behind the lateral fragment of the plateau and it was pulled back into the joint. A Schanz pin was placed into this lateral fragment to help rotate the fragment into the joint. A Cobb was used to elevate additional fragments of the articular surface. K wires were placed to hold everything together. Once intra-operative imaging confirmed reduction, a non-locking tibial plateau plate was secured in buttress mode to capture this posterior lateral fragment and secure it distally. The axilla of the fracture was captured with the plate, followed by screws proximally to add additional stable fixation (Figure 3). The wound was irrigated and closed in a layered fashion with a combination of Vicryl and clips.
Figure 3. A. AP B. Lateral. Intraoperative Fluoroscopic Images Illustrating the Non-Locking Tibial Plate Used
She was stable post-operatively and was non weight bearing bilaterally, with hinged knee brace on the right locked in extension to allow for soft tissue rest with plan for motion through the knee joint once the wound settled/sutures were removed. Physical therapy and occupational therapy evaluated her and recommended inpatient rehabilitation or home with 24-hour assistance. Day one post-operative, as psychiatry removed her Section 12, she left the hospital against medical advice and she was lost to follow-up thereafter.
DISCUSSION
Posterolateral tibial plateau fractures are caused by a valgus force with the knee in flexion, that leads to a shearing force between the lateral femoral condyle and the posterolateral plateau.8 Without surgical fixation, the fracture fragment will tend to move posteriorly and distally with knee motion, creating joint instability, pain, and neurovascular injury.9 As the conventional Schatzker classification system doesn’t account for posterior tibial plateau fractures, different classification systems have been proposed, one including a three-column classification,10 and one system developed by Hong-wei et al11 that classified posterolateral tibial plateau fractures by combining with CT reconstruction of the three dimensional (3D) images.11
While there is diversity in treatment options for posterolateral tibial plateau fractures, there are no definite treatment guidelines or algorithms in place. Rossman et al12 retrospectively analyzed 538 tibial plateau fractures fixed from 2012-2015 and found that fracture patterns could not reliably predict the choice of surgical approach, but rather relied on the surgeon’s experience, education, and preference. Cho et al13 proposed an algorithm for treating posterolateral tibial plateau fractures, advising certain surgical approaches based on injury type of either isolated posterolateral fragment (PLF), PLF with associated anterolateral plateau fracture, PLF with posterior shearing fracture, and PLF with bicolumnar plateau fracture.
Our patient had a unique fracture with posterior displacement of the fractured lateral tibial plateau behind a fractured fibular head. Asprinio et al14 described a similar case, where they used a direct posterior popliteal approach with buttress-plate fixation of the posterolateral fracture and a lateral approach to reduce the fracture, bone-grafting, and buttress-plate fixation of the lateral tibial plateau. Our case differs slightly in that the “posterior lateral” fragment involves essentially the entire lateral tibial plateau with the fibular head anterior to it. Performing a direct posterior approach would be difficulty as the fibular head would not be visualized and as such the block to reduction would not be able to be manipulated. An anterior approach would allow access to the fibular head, and with gentle anterolateral traction on the fibular head and a pull from posterior to anterior on the fractured tibial plateau fragment, we suspected that the fracture would reduce. This was essentially the case. The peroneal nerve was identified around the fibular head and entrapped between the fibular head and the tibial plateau posterior to it. A small sharp-sharp clamp was placed on the fibular head, and the head was pulled laterally, essentially out of the plane of the fracture. We then placed a long kidney clamp behind the dislocated anterolateral tibial plateau and hooked it, once it was securely hooked it was pulled in to place. The fibular head was then released and as the fibular head took its normal anatomic location it prevented further displacement of the fracture. We were then able to place a plate in buttress mode to secure the plateau.
CONCLUSION
Tibial plateau fractures with a displaced posterior fragment need special attention in diagnosis and management. These fracture patterns may not fit in previous classification systems. This unique fracture pattern was successfully fixed as outlined in this case report.
CONSENT
Written and verbal consent were unable to be obtained from the patient to reproduce information and photographs appearing in this article despite multiple attempts as the patient left against medical advice from the hospitalization and has been lost to follow-up since, with no healthcare proxy. Authors confirm that the submitted article is neither under consideration nor published previously.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.








