1. Yumuk Y, Tsigos C, Fried M, et al. European guidelines for obesity management in adults. Obes Facts. 2015; 8: 402-424. doi: 10.1159/000442721
2. World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight.Web site. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. Accessed September 29, 2017.
3. Prospective Studies Collaboration,Whitlock G, Lewington S, et al. Body-mass index and cause specific mortality in 900 000 adults: Collaborative analysis of 57 prospective studies. Lancet. 2009; 373: 1083-1096. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60318-4
4. Fried M, Yumuk Y, Oppert JM, et al. Interdisciplinary European guidelines on metabolic and bariatric surgery. Obes Facts. 2013; 6: 449-468. doi: 10.1159/000355480
5. Fruhbeck G, Toplak H, Woodward E, et al. Obesity: The gateway to ill health-an EASO position statement on a rising public health, clinical and scientific challenge in Europe. Obes Facts. 2013; 6: 117-120. doi: 10.1159/000350627
6. Dyson PA.The therapeutics of lifestyle management on obesity. Diabetes Obes Metabol. 2010; 12: 941-946. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01256.x
7. International Diabetes Federation (IDF). IDF Diabetes Atlas-2nd edition. Web site. www.diabetesatlas.org.component/attachments/task=download&id=73. Accessed September 28, 2017.
8. Possain P, Kawar B, El-NahasM. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world-a growing challenge. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356: 213-215. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp068177
9. Ziv E, Shafir E. Psammomys obesus (sand rat). [In:] Shafir E (ed) Nutritionally Induced NIDDM Like Syndrome on a Thrifty Gene Background in Lessons from Animal Diabetes. London, Smith Gordon: 1995; 5: 285-300.
10. Kalra S. Diabesity. J Pak Med Asson. 2013; 63(4): 532-541.
11. Oldridge NB, Stumb TE, Nothwehr FK, Clark DO. Prevalence and outcomes of comorbid metabolic and cardiovascular conditions in middle- and older-age adults. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001; 54: 928-934. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(01)00350-X
12. Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes(Lond). 2008; 32: 1431-1437. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.102
13. Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body mass index since 1980: Systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011; 377: 557-567. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5
14. Zimmet PZ. Diabesity and its drivers: The largest epidemic in human history? Clinical Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 3: 1. doi: 10.1186/s40842-016-0039-3
15. Anjana RM, Deepa M, Pradeepa R, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetesin 15 states of India: Results from the ICMR-INDIAB population-based cross-sectional study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 5: 585-596. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30174-2
16. Ma RC,Chan JC. Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: Similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2013; 1281: 64-91. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12098
17. Lim LL, Tan AT, Moses K, Rajadhyaksha C, Chan SP. Place of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 unhibitors in East Asians subjects with type 2 diabetes: Insights into management of Asian phenotypes. J Diabetes Complications. 2017; 31: 494-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.10.008
18. Abrahamian H, Kautuky-Willer A, Riesland-Seifert A , et al. Mental disorders and diabetes mellitus. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016; 128(suppl 2): S170-S178. doi: 10.1007/s00508-015-0939-8
19. Girlin M. Lithium side effects and toxicity: Prevalence and management strategies. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2016; 4: 27. doi: 10.1186/s40345-016-0068-y
20. Perez-Iglesias-R, Crespo-Facorro B, Martinez-Garcia O, et al. Weight gain indiced by haloperidol, risperidone and olanzapine after 1 year: Findings of a randomized clinical trial in a drug-naïve population. Schizophr Res. 2008; 99: 13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2007.10.022
21. El-Khatih F, Rauch enzauner M, Lechleitner M, et al. Valproate, weight gain and carbohydrate craving: A gender study. Seizure. 2007; 16: 226-232. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2006.12.009
22. Gaspari CN, Guerreiro CA. Modification in body weight associated with antiepileptic drugs. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2010; 68: 277-281. doi: 10.1590/S0004-282X2010000200024
23. Matson RH, Cramer JA, Collins JF. A comparison of valproate with carbamazepine in the treatment of complex partial seizures and secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures in adults. The department of vetaerans affairs epilepsy cooperative study No. 264 group. N Engl J Med. 1992; 327: 765-771. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209103271104
24. Lampi Y, Eshel Y, Rapaport A, Sarova-Pinhas I. Weight gain , increased appetite and excessive food intake induced by carbamazepine. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1991; 14: 251-255. doi: 10.1097/00002826-199106000-00009
25. Hamed SA. Antiepileptic drugs influence on body weight in people with epilepsy. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015; 8: 103-114. doi: 10.1586/17512433.2015.991716
26. De Toledo JC, Toledo I, De Cerce J, Ramsay RE. Changes in body weight with chronic, high dose gabapentin therapy. Ther Drug Monit. 1997; 19: 394-396. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199708000-00006
27. Baular M, Cavalcanti D, Semah F, Arzimanoglou A, Portal JJ. Gabapentin add on therapy with adaptable dose in 610 patients with partial epilepsy: An open observational study. The French gabapentin collaborative group. Seizure. 1998; 7: 55-62. doi: 10.1016/s1059-1311(98)90009-7
28. Berthon BS, MacDonald-Wicks LK, Wood LG. A systematic review of the effect of oral glucocorticoids on energy intake, appetite and body weight in humans. Nutr Res. 2014; 34: 179-190. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2013.12.006
29. Mana boriboon B, Silverman ED, Homsanit M, Chui H, Kaufman M. Weight change associated with corticosteroid therapy in adolescents with systemic lupus erythematosis. Lupus. 2013; 22: 164-170. doi: 10.1177/0961203312469260
30. Berenson AB, Rehman M. Changes in weight, total fat,percent body fat and central to peripheral fat ratio associated with injectable and oral contraceptive use. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009; 200: e1-329.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.12.052
31. Sharma AM, Pischon T, Hardt S, Kunz I, Luft EC. Hypothesis: Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers and weight gain: A systematic analysis. Hypertension. 2001; 37: 250-254. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.37.2.250
32. Blundell JE, Dulloo AG, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G. EASO SAB working group on BMI. Beyond BMI-phenotyping the obesities. Obes Facts. 2014; 7: 322-328. doi: 10.1159/000368783
33. Gomez-Ambrosi J, Silva C, Galotre JC, et al. Body mass index, classification misses subjects with increased cardiometabolic risk factors related to elevated adiposity. Int J Obes(Lond). 2012; 36: 286-294. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.100
34. Cameron AJ, Sicree RA, Zimmett PZ, et al. Cut-points for waist circumference in Europids and South Asians. Obesity(Silver Spring). 2010; 18: 2039-2046. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.455
35. World Health Orginazaion (WHO) Expert Consultation. Appropriate body mass index, for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004; 363: 157-163. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15268-3
36. Tsigos C, Hainer V, Basdevant A, et al. Management of obesity in adults: European clinical practice guidelines. Obes Facts. 2008; 1: 106-116. doi: 10.1159/000126822
37. Yumuk Y, Fruhbeck G, Oppert JM, Woodward E, Toplak H. An EASO position statement on multidisciplinary obesity management in adults. Obes Facts. 2014; 7: 96-101. doi: 10.1159/000362191
38. Beaudart C, McClosekey E, Bruyere O, et al. Sarcopenia in daily practice assessment and management. BMC Geriatr. 2016; 16: 170. doi: 10.1186/s12877-016-0349-4
39. Morley JE, Anker SD, Von Haehling S. Prevalence, incidence and clinical impact of sarcopenia: Facts, numbers and epidemiology update 2014. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2014; 5: 253-259. doi: 10.1007/s13539-014-0161-y
40. Malmstrom TK, Miller DK, Simonsick EM, Ferucci L, Morley JE. SARC-F: A symptom score to predict persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2016; 7: 28-36. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12048
41. Otto M, Kautt S, Kremer M, Kienle P, Post S, Hasenberg T. Handgrip strength as a predictor for post bariatric body composition. Obes Surg. 2014; 24: 2082-2088. doi: 10.1007/s11695-014-1299-6
42. Portier P, Despres JP. Exercise in weight management of obesity. Cardiol Clinic. 2001; 19: 459-470. doi: 10.1016/S0733-8651(05)70229-0
43. Willis LH, Stentz CA, Bateman LA, et al. Effect of aerobic and/or resistance training on body mass and get mass in overweight and obese adults. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012; 113: 1831-1837. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01370.2011
44. Geliebter A, Ochner CN, Dambkowski CL, Hashim SA. Obesity-related hormones and metabolic risk factors: A randomized trial or diet plus either strength or aerobic treaining versus diet alone in overweight participants. J Diabetes Obes. 2014; 1: 1-7.
45. Look AHEAD Research Group. Eight year weight loss with an intensive lifestyle intervention: The look AHEAD study.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014; 22: 5-13. doi: 10.1002/oby.20662
46. Shai I, Schwarzfuchs D, Henkin Y, et al. Weight loss with a low carbohydrate, Mediterranean, or low fat diet. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359: 229-241. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708681
47. Larsen RN, Mann NJ, Maclean E, Shaw JE. The effect of a high protein, low carbohydrate diets in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A 12 month randomized controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2011; 54: 731-740. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-2027-y
48. Krebs JD, Elley CR, Parry Strong A, et al. The Diabetes Excess Weight loss(DEWL)Trial: A randomized Controlled trial of high protein, versus high carbohydratediets over 2 years in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012; 55: 905-914. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2461-0
49. Esposito K, Maiorino MJ, Ciotola M, et al. Effects of a Mediterranean-style diet on the need for antihyperglycaemic druf therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151: 306-314. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-5-200909010-00004
50. Belwal T, Nabavi SF, Nabavi SM, Habtemariam H. Dietary anthocyanins and insulin resistance: When food becomes a medicine.Nutrients. 2017; 9: e1111. doi: 10.3390/nu9101111
51. Clark JL, Taylor CG, Zahradka P. Rebelling against the (insulin)resistance: A review of the proposed insulin-sensitizing actions of soybeans, chickpeas, and their bioactive compounds. Nutrients. 2018; 10: e434. doi: 10.3390/nu10040434
52. Low JY, Lacy KE, McBride RL, Keast RS. Carbohydrate taste sensitivity is associated with starch intake and waist circumference in adults. J Nutr. 2017; 147: 2235-2242. doi: 10.3945/jn.117.254078
53. Low JY, Lacy KE, McBride RL. The associations between oral complex carbohydrate sensitivity, BMI, liking and consumption of complex carbohydrate based foods. J Food Sci. 2018; 83: 2227-2236. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14276
54. Dansinger ML, Gleason JA, Griffith JL, Selker HP, Schaefer EJ. Comparison of the atkins, ornish, weight watchers and zone diets for weight loss and heart disease risk reduction: A randomized trial. JAMA. 2005; 293: 43-53. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.1.43
55. Habtemariam H. Could we really use aloe vera food supplements to treat diabetes? Quality control issues. Evidence Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2017; 2017: doi: 10.1155/2017/4856412
56. Wadden TA, West DS, Neiberg RH, et al. One year weight losses in the look AHEAD study: Factors associated with success.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009; 17: 713-722. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.637
57. Wycherley TF, Buckley ID, Noakes M,Clifton PM, Brinkworth GD. Long term effects of a very low carbohydrate weight loss diet on exercise capacity and tole rance in overweight and obese adults. J Am Coll Nutr. 2014; 33: 267-273. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2014.911668
58. Kaur KK, Allahbadia GN, Singh M. Weight loss associated with high protein intake in obesity: Interactions of gut microbiota in protein sources influencing this positive effect. Acta Scientific Nutritional Health. 2018; 2: 80-89.
59. Cawthon PM, Fox KM, Gandra SR, et al. Do muscle mass, muscle density, strength and physical function similarly influence risk of hospitalization in older adults? J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57: 1411-1419. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02366.x
60. Bellfiore A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L,Vigneri R. Insulin receptor isoforms nd insulin receptors/insulin like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev. 2009; 30: 586-623. doi: 10.1210/er.2008-0047
61. Signeri R, Goldfine ID, Frittita I. Isulin, insulin receptors and cancer. Endoc Invest. 2016; 39: 1365-1376. doi: 10.1007/s40618-016-0508-7
62. Hainer V, Toplak H, Stitch V. Fat or fit: What is more important? Diabetes Care. 2003; 26: 3230-3236. doi: 10.2337/dc09-S346
63. Servan PR. Obesity and diabetes. Nitr Hosp. 2013; 28 Suppl5: 138-143. doi: 10.3305/nh.2013.28.sup5.6929
64. Farr OM, Mantzoros CS. Treatment options to prevent diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: Efficacy, cost effectiveness and future outlook. Metabolism. 2017; 70: 192-195. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.12.017
65. Lindstrom J, Louheranta A, Mannelin M, et al. The finnish diabetes prevention study (DPS): Lifestyle interventions and 3-year results on diet and physical activity. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26: 3230-3236. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.12.3230
66. Knowler WC, Barrett-Conoor E, Fowler SE, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346: 393-403. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012512
67. Leom ME, Powme JK, Anderson AS, Garthwatt PH. Obesity, weight loss and prognosis in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 1990; 7: 228-233. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01375.x
68. Williamson DF, Thompson TJ, Thun M, Flanders D, Pamuk E, Byers T. Intentional weight loss and mortality among overweight individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23: 1499-1504. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.10.1499
69. Wing RR, Lang W, Wadden TA, et al. Benefits of modest weight loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34: 1481-1486. doi: 10.2337/dc10-2415
70. Look AHEAD Research Group, Wing RR. Long-term effects of a lifestyle interventions on weight and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Four year results of the Look AHEAD trial. Arch Int Med. 2010; 176: 1566-1575. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.334
71. Bristor GD, Borraidale KE, Sanders MH, et al. A randomized study on the effect of weight losson obstructive sleep apnea among obese patients with type 2 diabetes: The sleep AHEAD study. Arch Int Med. 2009; 169: 1619-1626. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2009.266
72. Rubin RR, Wadden TA, Bahnson JL, et al. Impact of intensive lifestyle interventions on depression and health related quality of life in type 2 diabetes: The Look AHEAD trial. Diabetes Care. 2014; 31: 1544-1553. doi: 10.2337/dc13-1928
73. Franz MJ. The role of weight loss in the management of type 2 diabetes. US Endocrinol. 2016; 12: 14-15. doi: 10.17925/USE.2016.12.01.14
74. Arab L, Dhaliwal SK, Martin CJ, Larios AD, Jackson NJ, Elashoff D. Association between walnut consumption and diabetes risk in NHANES. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018; 34: e3031. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3031
75. Farr OM, Tuccinardi D, Upadhyay J, Oussada SM, Mantzoros CS. Walnut consumption increasesactivation of the insula to highly desirable food cues: A randomized, double blind placebo-controlled crossover fMRI study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20: 173-177. doi: 10.1111/dom.13060
76. Garg SK, Maurer H, Reed K, Selagamsetty R. Diabetes and cancer: Two diseases with obesity as a common risk. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16: 97-110. doi: 10.1111/dom.12124
77. Eeg-Oloffson K, Cederholm J, Nilsson PM, et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes: An observational study in 13,087 patients.Diabetologia. 2009; 52: 65-73. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1190-x
78. Toplak H, Hoppichler F, Wascher TC, Schindler K, Ludvuk B. Obesity and type 2 diabetes. . 2016; 128(supp2): S196-200. doi: 10.1007/s00508-016-0986-9
79. Kaur KK, Allahbadia GN, Singh M. Current management of obesity in an infertile female-recent advances and future prospective drugs. Journal of Pharmacy and Nutrition Sciences. 2013; 3: 1-13.
80. Kaur KK, Allahbadia GN, Singh M. An update on a etiopathogenesis and management of obesity. Obesity and Control Therapies:Open Access. 2016; 3: 1-17. doi: 10.15226/2374-8354/2/2/00123
81. Van Gaal L, Seneen A. Weight management in type 2 diabetes: Current and emergomg approaches to treatment. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38: 1161-1172. doi: 10.2337/dc14-1630
82. Ahren B, Atkin SL, Charpentier G, et al. Semaglutide induces weight loss in subjects with type 2 diabetes regardless of baseline BMI or gastrointestinal adverse events in the SUSTAIN 1 to 5 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20: 2210-2219. doi: 10.1111/dom.13353
83. Kaur KK, Allahbadia GN, Singh M. An update on bariatric surgery with long term efficacy and its utilization for medical therapy development from the different mechanism of action and other short comes to be outcome. BAOJ Surgery. 2018; 4: 038.
84. Buchwald H, Avdor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004; 292: 1724-1737. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.14.1724
85. Bayhan BE, Greenway FL, Bellanger DE, O’Neil CE. Early resolurion of type 2 diabetes seen after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012; 14: 30-34. doi: 10.1089/dia.2011.0151
86. Munzberg H, Laque A, Yu S, Rezat-Zadeh K, Berthoud HR. Appetite and body weight regulation after bariatric surgery. Obes Rev. 2015; (Suppl 1): 77-90. doi: 10.1111/obr.12258
87. Mathes CM, Spector AC. Food selection and taste changes in humans after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A direct measure s approach. Physiol Behav. 2012; 107: 476-483. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.02.013
88. Sjoholm K, Pejmen P, Karason R, et al. Incidence of remission in type 2 diabetes in relation to degree of obesity at baseline and 2 year weight change: The swedish obese subjects (SOS) study. Diabetologia. 2015; 48: 1448-1455. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3591-y
89. Thibault R, Huher O, Azagury DE, Pichard C. Twelve key nutritional features in bariatric surgery. Clin Nutr. 2016; 35: 12-17. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.02.012
90. Schauer PR, Bhatt DI, Karwan JP, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes -5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376: 641-651. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1600869
91. Haner WS. Vitamin A signaling and homeostasis in obesity, diabetes, and metabolic disorders. Pharmacol Ther. 2019; S0163-7258: 30012-30019. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.01.006
92. Dakshinamurti K. Vitamins and their derivatives in the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome diseases (diabetes). Can J Physiol Pharmaciol. 2015; 93: 355-362. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0479
93. Cione E, Caroleo MC, Cannataro R, Perri M, Pingitore A, Genchi G. Viatamin A and diabesity: New insights for drug discovery.Mini Review Med Chem. 2016; 16: 738-742. doi: 10.2174/1389557515666150709112822
94. Holsky S, Ellis SI. Obesity, indulin resistance and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Diabetes Obes. 2015; 22: 277-282. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000170
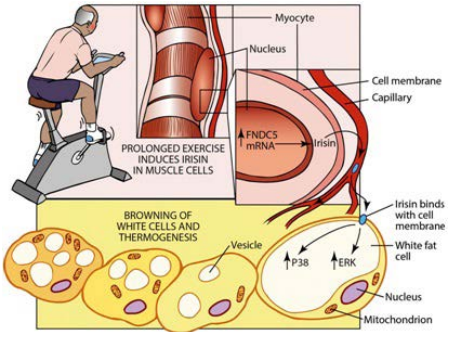
95. Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, et al. A PGC1-α dependent myokine that drives brown fat like development of white fat thermogenesis. Nature. 2012; 481: 463-468. doi: 10.1038/nature10777