INTRODUCTION
Aphasia is an acquired language disorder that affects mostly one-third of the patients suffering from stroke.1,2 Traditionally, aphasia has been studied in domains related to linguistic manifestations that are interpreted by applying the concept of models concerning cognitive or neuroscience-based neuropsychology.3,4,5 Wernicke’s aphasia (WA) is a disorder that results in severe impairment regarding language production and comprehension. Conventionally, impaired-based measures are been extensively used by speech-language pathologists (SLPs) as outcome tools to tabulate the outcome of intervention plan being implemented for people with aphasia (PWA) and to provide detailed insight regarding the status of an individual’s communication function.6,7,8,9 Although the various impaired-based language measures (e.g., Western Aphasia Battery–Revised (WAB-R)10,11 generally furnish information to strengths and weaknesses related to language abilities for making a proper diagnosis, it has been observed that the outcomes of these language-based test measures often cannot adequately document the subjective practical difficulties encountered by persons with aphasia.12,13,14,15
International Classification of Functioning (ICF), Disability, and Health is a classification of human functioning and disability. ICF defines components as “Health domains” and “Heath-Related domains”. It is a biopsychosocial approach, which attempts to achieve a synthesis, to provide a coherent view of different perspective of health from biological, individual and social perspective.16,17,18,19 The health domains and heath related domains of ICF described from the perspective of the body, the individual and society in two basic lists: 1. Body function and Structures; 2. Activities and participation.19 Individuals with aphasia tend to exhibit both body structure function impairment which restricts their activity (psychological consequences as well as social restrictions).20 The impact of aphasia on family members and spouse is also acknowledged.18,21 The most appropriate people for judging meaningful changes in life participation are PWA themselves.22,23 A review study was conducted by Hilari et al24 in which most of the research papers indicated that emotional distress, aphasia severity, and communication disability, activity limitations, associated medical problems, and family/social support are to be major factors in determining impact of aphasia on quality of life (QoL).
Currently, there is a lack of evidence regarding effective aphasia treatment outcomes and a lack of consensus amongst clinicians about what constitutes a meaningful treatment outcome. The World Health Organization’s (WHO) ICF19,25,26 provides a thought-provoking framework for this kind of intervention plan, wherein disability is defined in terms of multiple dimensions, including activities and participation. Impaired communication skills, which is the most evident functional outcome in persons with aphasia, which has mostly been studied under the impairment domain of ICF; for example, while confronting non-verbal and verbal communication, or while examining to what extent non-verbal communication.25,26,27,28,29 The present case-study aimed to highlight the insights into verbal communication activity in patients diagnosed with Wernicke’s aphasia with an attempt to understand which activities are the most or least affected followed by a detailed intervention plan focusing on all the areas especially on activities of the ICF domain. The individuals who participated for the current study were chosen from an speech and language intervention centre located in the capital of India.
METHODS
Case 1
The patient was a 60-year-old right-handed male retired banker and a well-established political family background and social environment. Informed verbal consent from the subject and subject’s caregiver was taken and both of them were willing to participate in this study. The individual suffered from a stroke soon after bypass surgery 2-months before the commencement of therapy sessions. Computed tomography (CT) scan performed after revealed acute infarct of embolic-left temporal-left insular and left frontoparietal lobe. Two months post-injury, the patient presented with the characteristics of Wernicke’s aphasia with restricted speech. At a conversational level, the patient exhibited preserved language comprehension, borderline fluent speech with paraphasias, perseveration, and word repetitions. Sometimes the individual used to sporadically communicate through gesture and facial expression. He required the listener to initiate any topic, ask yes/no questions, and sometimes clarify the message given or received. Post-stroke he retained the ability to use gesture and 1-month post-injury he was able to communicate through words with paraphasic errors as well as was able to follow the musical note of familiar songs.
Neuropsychological Profile
The WAB–R11 scores of the patient revealed that language problems are related to expression as well as comprehension. The components of WAB which includes components like auditory comprehension, answering yes-no question was severely affected. The patient was expressive but circumlocutory errors were present. The individual also exhibited core word retrieval problems typical of classical Wernicke’s aphasia in the expressive domain, the individual revealed poor verbal ability with paraphasias. The patient was able to read aloud phrases, name of the objects, or but had difficulty in responding to simple questions even though he exhibited that he knew the answers.
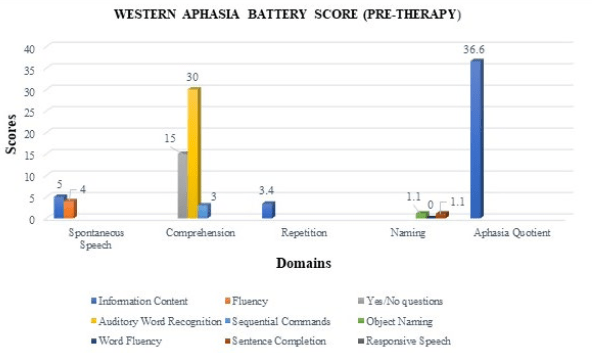
The writing skills seemed to be collateral to his spoken speech; he could copy words and could write words but not compose his sentences, was able to write own name and serial sequences without copying, but could not write to dictation or perform simple written tasks of WAB. Concerning the receptive domain, patient’s comprehension difficulties were most evident on the ideational material task, which requires a yes/no response to questions related or unrelated to the immediate context. The participant also couldn’t follow group conversations with ease, highlighting the inability to understand speech using contextual cues. As indicated in Figure 1 he exhibited fair performance on the tasks related to written comprehension tasks, matching printed words with pictures or spoken words and choosing the suitable word to ‘fill the gap’ in sentences were familiar and limited.
Figure 1. Assessment of Language Skills Using the Western Aphasia Battery which Shows the Individual Performance on the Tasks Related to Written Comprehension Tasks, Matching Printed Words with Pictures or Spoken Words and Choosing the Suitable Word to ‘Fill the Gap’ in Sentences were Familiar and Limited Compared to Other Domains like Repetition, Naming and Spontaneous Speech which Reflected Poor Scores.
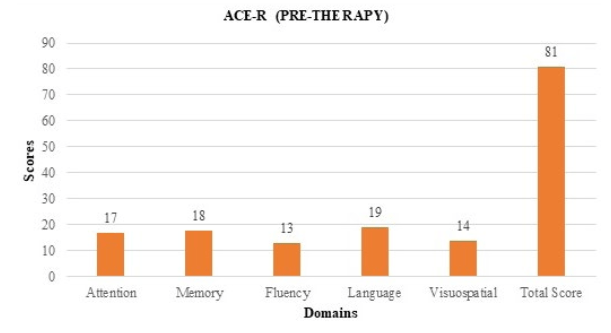
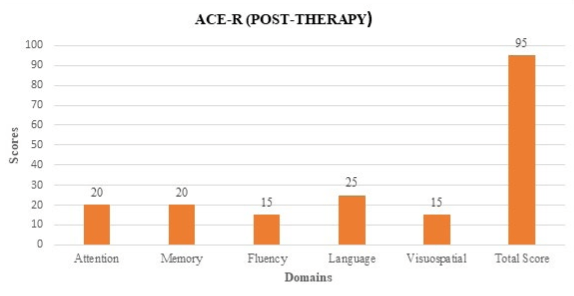
The Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Revised (ACE-R) was also administered on the individual to evaluate the key aspects of cognition.30 The scores obtained in language were poor as repetition and object naming was affected. Memory, visuospatial skills and verbal fluency were also affected. The individual was unable to copy loop-based pictures which was presented to him in the form of pictures. Overall score obtained in ACE-R shown in Figure 2 suggested mild cognitive impairment which indicated that the individual had difficulties in spontaneous naming, long-term memory (e.g., “what is your date of birth?” etc.) verbal fluency which in turn restricted his daily activities and affected the QoL.
Figure 2. Assessment of Cognitive Skills Using ACE-R Reveals Individual Exhibited Difficulties in Certain Domains like Spontaneous Naming, Long-term Memory (E.g., “what is your birth place?” etc.) Verbal Fluency Along with Poor Visuospatial Performance.
Quality of Life
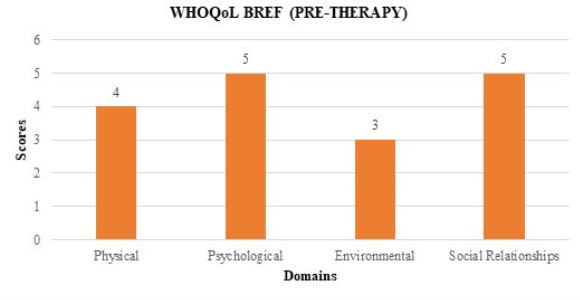
As the subject exhibited poor linguistic ability and was unable to establish effective communication, it was affecting his day-to-day activities. The patient had to be dependent on the caregiver to initiate or maintain any significant topic or implement any task. According to the ICF19 Framework, World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL-BREF) questionnaire31 was being framed to assess the impact of severity of aphasia on individual’s perception of QoL. The scores obtained in each domain shown in Figure 3 revealed that the severity of aphasia has a crippling effect on social relationships resulting in stress and depression in the individual.
Figure 3. Assessment of QoL Using WHOQoL-BREF Shows that the Individual had an Negative Impact on Psychological Issues and also was Facing Difficulty in Maintaining Social Relationships (like Meeting Friends, Restriction Regarding Social Visits) Due to Impaired Communication which in Turn Resulted in Depression and was Affecting the Quality of Life.
Procedure
Intensive functional treatment approach was framed by an experienced Speech Language Pathologist for eight sessions/ one hour exclusively for 2-months with the goals to improve the linguistic abilities and cognitive skills. The intervention plan was framed considering the ICF framework, the goals were designed to assist the individual to achieve the highest level of independent function for participation in daily living.
Intervention goals were designed based on:
- Capitalize on strengths and address weaknesses related to underlying structures and functions that affect communication across partners, activities, and settings;
- Facilitate the individual’s activities and participation by (a) teaching new skills and compensatory strategies to both the individual with aphasia and his or her partner(s) and (b) incorporating augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) strategies if appropriate; and
- Modification of contextual factors that might serve as barriers and enhance those that facilitate successful communication and participation, including accommodations such as large print, pictures, and aphasia-friendly formatting to support comprehension of written health materials.32
Thus the therapy sessions consisted of three core therapy techniques with approaches divided into two categories i.e. restorative and compensatory aimed at improving impairments focus on “body functions/structures and “activities/participation.” The specific techniques were: (i) Treatment for Wernicke’s Aphasia (TWA) (ii) Deblocking (iii) Promoting Aphasics’ Communication Effectiveness (PACE) and AAC. The therapy sessions took place in three phases which follows:
Phase-I-enhancing positive attitude towards the problem and encouraging caregiver support: Initially, the therapy begins with approaches that engage communication partners to facilitate improved communication in persons with aphasia. Caregiver were trained to encourage multimodal communication to improve social interaction and also helps the person with aphasia to re-engage in life through daily participation in activities of his or her choice.
Phase-II-application of therapy approach: The individual with aphasia and the clinician take turns as the message sender or receiver. Picture prompts for conversational messages are hidden from the listener (similar to a barrier task), and the speaker uses his or her choice of modalities for conveying messages.33 Picture communication, pointing, use of printed words were used as the a choice of communication at the initial phase. The concept of TWA created by Helm-Estabrooks et al34 was introduced in the session. A corpus of words printed in lowercase was selected and was presented to the client followed which the client was encouraged to read aloud along with the respective pictures. Since the individual exhibited poor auditory comprehension skills, henceforth those printed cards of the same words (e.g., “Table”, “brush”, “chasma”, “bed” etc) were repeated and the individual was again asked to select the picture and was asked to read the printed word aloud.
The card was then turned over and the participant was asked to replicate to improve his auditory identification and comprehension skills. This activity was performed again in which clinician uttered the target word (e.g., “chasma”, “bed” etc.) and the subject had to point to the picture. He exhibited better performance on the tasks related to written comprehension tasks, matching printed words with pictures or spoken words and choosing the suitable word to ‘fill the gap’ in sentences that were familiar with proper association.
Apart from TWA, language facilitation was also carried out using deblockidng method.33 In this technique, several unrelated words were presented which was known to the patient was presented at the initial phase followed by the target word for the subject to respond accordingly. As any mode of expression, it was observed that the use of gestures and phonetic cues to deblock auditory commands yielded encouraging outcomes.
Cueing strategies were also used to improve the naming task. Various noun pictures were presented followed by verb pictures. Initially, semantic cues were given and if still, the response was not there then phonemic cues were provided to get the name of the stimulus.
Phase-III-stabilization and carry over: The third and most important phase of the therapeutic regime was focused on stabilization and carryover of available mode of communication (verbal along with occasional gestures) to conventional expressive and receptive language. The patient now tries to use verbal cues along with gestures to express. Roles of speaker and listener were exchanged to ensure that the individual’s auditory comprehension skills have improved; thus resulting in effective communication significantly having a better QoL according to ICF.
RESULT
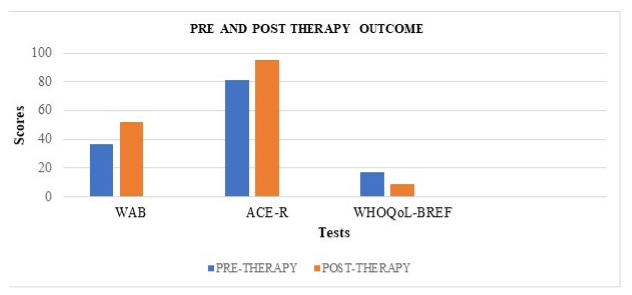
Overall, as indicated in Graph 4, the performance of PWA was significantly better following the intensive treatment. A detailed summary of outcomes on standardized assessments measures as follows:
Western Aphasia Battery–Revised
With intensive treatment of 8 sessions for 2-months, the subject showed significant improvements in WAB-R as shown in Table 1 and Figures 4 and 5. Overall, the PWA’s AQ improved by 15 points when compared to pre-treatment baseline result. A change of 5 or more AQ points has been considered to be significant clinically.34 An AQ of 51.8 corresponds to the diagnosis of conduction aphasia.
| Table 1. Comparison of Assessment Scores of WAB |
|
Subtests
|
Pre-therapy Scores |
Post-therapy Scores
|
| Information Content (/10) |
5
|
6
|
| Fluency (/10)1 |
4
|
5
|
| Spontaneous Speech (/20) |
9
|
11
|
| Yes/No Questions (/60) |
15
|
20
|
| Auditory Word Recognition (/60) |
30
|
40
|
| Sequential Commands (/80) |
3
|
10
|
| Auditory Verbal Comprehension (/200) |
48
|
70
|
| Repetition (/100) |
34
|
42
|
| Object Naming (/60) |
10
|
24
|
| Word Fluency (/20) |
0
|
3
|
| Sentence Completion (/10) |
1
|
2
|
| Responsive Speech (/10) |
0
|
2
|
| Naming and Word Finding (/100) |
11
|
3.1
|
| Aphasia Quotient |
36.6
|
51.8*
|
| *Indicates improvement of +5 AQ points following treatment. A change of 5 or more points is considered to be clinically significant.37 |
Figure 4. Assessment of Language Skills Using the Western Aphasia Battery which Reflects Improved Scores Across All Domains
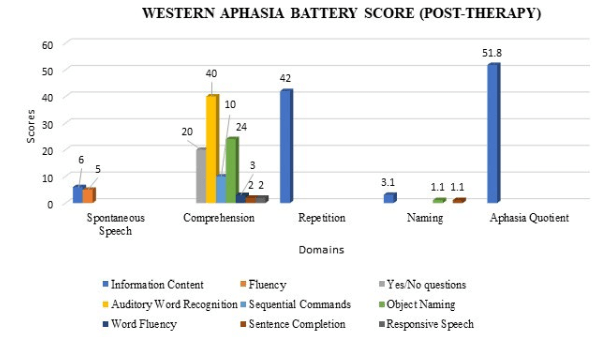
Figure 5. Comparison of Scores of Standardised Test(s) of Pre Therapy and Post-therapy Outcomes Based Upon the Scores Obtained shows Significant Improvement in Each Domain of the Three Standardized Tests Which was Administered on PWA Post-intensive Therapy Sessions
Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination-Revised
The language and memory domains, as well as the visuospatial domains, were re-assessed during follow-up testing. The results were compared to post-therapy outcomes as shown in Table 1.1 and Figure 5 and Figure 6. There was a significant improvement in scores of language and memory domain. There was a slight decrease in performance in the fluency domain, but it was not significant.
| Table 1.1. Comparison of Assessment Scores of ACE-R |
|
Subtests
|
Pre-therapy Scores |
Post-therapy Scores
|
| Attention |
17
|
20
|
| Memory |
18
|
20
|
| Fluency |
13
|
15
|
| Language |
19
|
25
|
| Visuospatial |
14
|
15
|
| Total |
81
|
95
|
Figure 6. Assessment of Cognitive Skills Using ACE-R Reveals Significant Improved Scores in All Sections of ACE-R
WHO-QoL BREF
Domains of physical; ability to learn new things; communication of basic needs; and positive attitude towards the problem improved slightly. Outcomes from the follow-up assessment shown in Table 1.2 and Figure 5 indicated that the PWA still felt better support in his spousal relationship than immediately following treatment.
| Table 1.2. Comparison of Assessment Scores of WHO-QoL |
|
Subtests
|
Pre-therapy Scores |
Post-therapy Scores
|
| Physical |
4
|
3
|
| Psychological |
5
|
2
|
| Environmental |
3
|
2
|
| Social relationships |
5
|
2
|
| Total |
17
|
9
|
DISCUSSION
Outcomes following the treatment program were compared to pre- and post-standardized assessment test results to determine if the severity of aphasia decreases leading to better QoL based on the ICF framework. The patient’s language, cognitive-linguistic skills, functional communication, perceived QoL, physical, psychological and communicative effectiveness were evaluated. Results showed significant improvements in language, memory, functional communication skills, perceived QoL, and psychological domains following independent functional-based treatment regime with the patient. For physical and communication domains improvement is seen to occur within 3-months from the onset of acute stroke tends to exhibit greater improvement if treatment is given intensively and routine is maintained.29,35,36
Our results agree with many studies in the literature that underline that the frequency of depression in aphasic patients is higher than in other stroke survivors.35,37,38,39,40,41,42 Similar study was conducted by Hilari et al46 where in the authors compared life before stroke and with post-stroke, regardless of their aphasia severity, results indicated that individuals with aphasia expressed that living with aphasia impacts all aspects of life participation (i.e., reduced participation at home/society, negative attitude, communication difficulties, and increased environmental barriers.35,44,45 PWA often demonstrates co-existing cognitive difficulties which was also observed during our baseline assessment. Current study findings revealed that the result of memory and language comprehension in ACE-R and WAB is related to positive QoL.35,46,47,48,49,50 The result of the present study emphasizes the importance of effective treatment routine to examine current life participation and assess meaningful life changes for adults with mild to severe aphasia.
LIMITATIONS
Results from this study cannot be generalized as this study was a single-case study. Results may not be generalizable to other individuals with aphasia or with different time onset of stroke. Besides, PWA had received group and individual intervention for 2-months before the start of this study. Outcomes from these intervention plans might influence pre-treatment baseline outcomes including the neuroimaging investigation (CT scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)), post-therapy neuroimaging investigation was not conducted in this study which could have provided a better insight regarding the effectiveness of the speech therapy. Additionally, a longer treatment period or greater treatment intensity might contribute to greater gains and/or maintenance of the outcome.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR FUTURE RESEARCH
Future research should include larger sample sizes with PWAs with different types and severities of aphasia who received similar pattern of treatment and a placebo group which can provide insight regarding the outcome in an more informative manner. Future research can also focus on whether an increase in intensity and duration of treatment would improve outcomes and maintain gains concerning QoL. If subjects have received previous therapy from an unknown source, a washout period should be considered before pre-treatment baseline measures are obtained.
CONCLUSION
Results of the present study support previous research findings which suggest that evidence-based treatment plan with a PWA may lead to improvements in communication skills. It’s highly recommended that evidence-based treatment plan with a PWA can be effective in improving QoL which is an important component of the World Health Organization’s International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (WHO-ICF). SLPs can become more efficient with patient-reported measures appropriate for PWA, implement skilled support to maximize the PWA competence and include confidence measures which include life participation, cognition, and communicative measures as standard components of aphasia evaluation to better understand PWA’s priorities in life for aphasia treatment and establish better QoL.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.











