INTRODUCTION
Multiple myelomas are a hematologic malignancy that originates in the plasma cells. In recent years, the appearance of novel drugs has led to improvements in therapeutic outcomes, but these outcomes remain insufficient in the case of elderly and patients with complications. However, novel drugs such as Bortezomib (Bor) and Lenalidomide (Len) may represent new therapeutic strategies and their appearance means that their single and combined use provides a wider range of drug options. In particular, the immunomodulatory drug (Imid), Len, is an oral drug that is highly beneficial to elderly patients and patients who live in remote areas with poor access to the hospital, and for this reason, it has become a key drug.
Dimopoulos and Weber have reported that the efficacy of Len, when used in combination with Dexamethasone (Dex), is an improvement over Dex monotherapy when used on new multiple myeloma.1,2 In addition, the FIRST study, which conducted a comparison of melphalan, prednisolone and thalidomide (MPT) and Ld (Lenalidomide and Dex), verified the efficacy of Ld.3 VRd therapy, which combines Ld with Bor, is also thought to be an effective therapy.4 In recent years regimens that combine Ld with Darazalex, Carfilzomib, Ixazomib, Elotuzumab, and other drugs have been attempted. Thus, the issue of which drug to combine with Lenalidomide is important. Currently, there are cases – such as the elderly or those with particular circumstances – who are unable to utilize novel drugs.
Clarithromycin (CAM) is an oral drug that is already available and as a result, it is easy to use. When CAM is used in combination with corticosteroids it is thought to have an optimizing action on the pharmacological effect of the corticosteroid by increasing the area under the curve (AUC) and the maximum blood concentration of the steroid. It also has the characteristics of an immunomodulator and suppresses inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 in particular. CAM may also induce cell death by autophagy, and it has been shown to have a direct antitumor effect.5,6,7,8 Rossi reported on Clarithromycin, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (Bird) therapy, in which CAM is used in combination with Ld therapy, for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients.9 They indicated that it is highly effective, with a total response rate of 90% and CR of 39%. However, there are few data on its efficacy and safety in Japanese patients. Niesvizky used a CAM initial dose of 1,000 mg/day with Bird therapy in a Phase II trial, CAM dose is mostly used at 400 mg/day.10 Therefore, in the present study we assessed the efficacy and safety of Bird therapy with CAM 400 mg/ day when used on the Japanese elderly, those with complications, and those who live in remote areas to visit the hospital.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
We analyzed 7 patients with relapsed refractory or new refractory multiple myeloma who were visited at this hospital between January 2012 and December 2014. We obtained informed consent from all patients in writing. Treatment was performed a 28-day cycle, with CAM 400 mg/day for 28-days and Len 15 mg/day for 21-days, with a drug rest of 7-days. Dex was administered in a dose of 20 mg/dose once per week. The Len and Dex doses were increased or decreased on the determination of the attending physician. All patients were registered in Rev-Mate and the required safety management guidelines were followed. Low dose aspirin is recommended to prevent thrombosis. The use of granulocytecolony stimulating factor (G-CSF) was administered at the physician’s discretion for adverse events of neutropenia. The response criteria used were standard International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) uniform response criteria. and adverse events were graded according to the national cancer institute-common terminology criteria for adverse events (NCI-CTCAE) Ver. 4. Statistical analysis was performed using Easy R (EZR).11
The primary outcome measures were response rate and safety, and the secondary outcome measure was overall survival rate.
The exclusion criteria were: patients with uncontrollable disease complications and patients with a history of allergy to macrolide antibiotics.
RESULTS
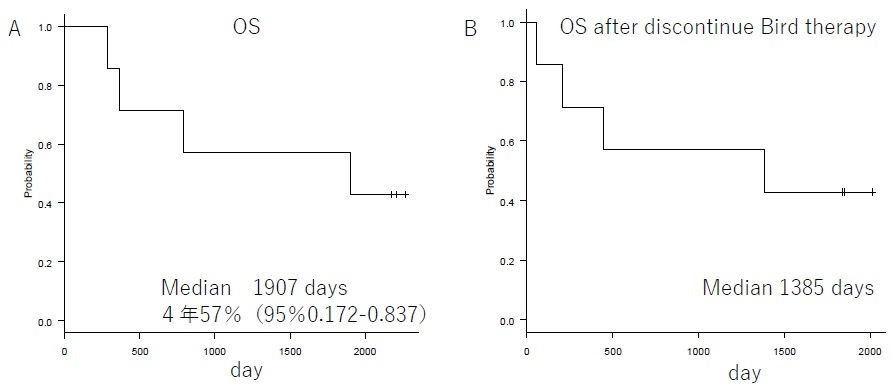
Patient background characteristics are shown in Table 1. The enrolled patients consisted of 4 with relapsed refractory disease and 3 with new refractory disease. Bone lesions were observed in all patients. Patients with the new refractory disease were started on Bird therapy after administration of Dex monotherapy (20 mg for 4-days). Patients who already underwent a regimen that included Bor/Imids as the prior therapy were 4/2 patients respectively. Two patients underwent at least 3 regimens, and 1 patient underwent autologous transplantation. None of the patients had kidney dysfunction of creatinine 2 mg/dL or above. The reason for drug switching in the relapsed group was progression disease. No drug switching was done as a result of adverse effects (AE). The M protein decreased rapidly from 3711 mg/dL to 1305 mg/dL on average after one cycle (Figure 1). For the relapsed patients, the best effects of the prior therapy were CR/VGPR/PR in 1/1/2 patients respectively. The best response is shown in Table 2. The results were sCR/CR/PR /SD in 2/1/3/1 patients respectively. Response rates of per rectum (PR) or better was observed in 86% of the patients, indicating sufficient therapeutic efficacy. The mean duration of response was 316-days (range, 160-522-days). The median oculus sinister (OS) during the follow-up period of April 30, 2019 was 1,907-days. The median OS after the conclusion of the Bird therapy was 1,385-days (Figure 2). Currently, 3 patients are still alive. The mean number of treatment cycles was 10 cycles. Prior therapy consisted of 2 regimens.
Figure 1. The Change of M Protein After One Cycle. The Average was 3711 mg/dl in Before and 1305 in After
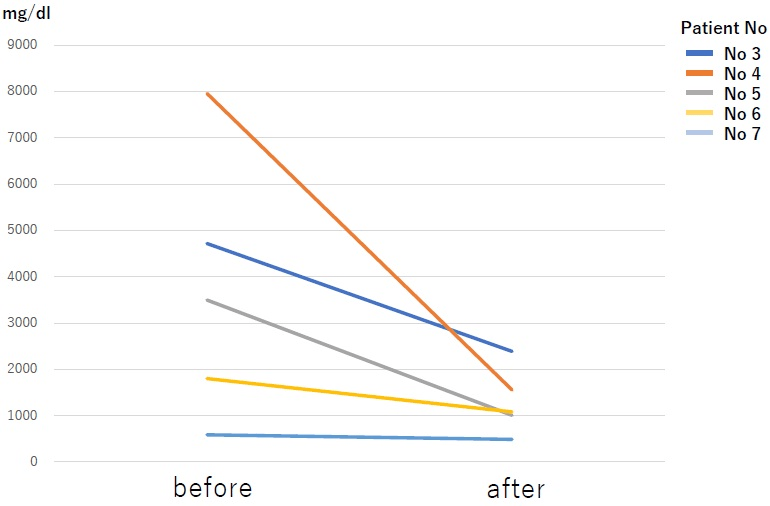
Figure 2. OS. Panel A Shows OS of Bird Therapy. Panel B Shows OS After Discontinue Bird Therapy
Safety
Adverse events are shown in Table 3. Hematological adverse events were as follows: Anemia of Grade (G) 1-2 was observed in 3 patients and anemia of G3-4 was observed in 1 patient. Thrombocytopenia of G1-2 was observed in 1 patient and thrombocytopenia of G3-4 was observed in 1 patient. Leukopenia of G1-2 was observed in 6 patients and leukopenia of G3 was not observed. Investigation of non-hematological adverse events indicated that 6 patients had G1-2 liver dysfunction, 3 patients had a G1-2 skin rash, and 2 patients had G1-2 constipation, G-4 adverse events were fainting and duodenal ulcer in 1 patient each.
DISCUSSION
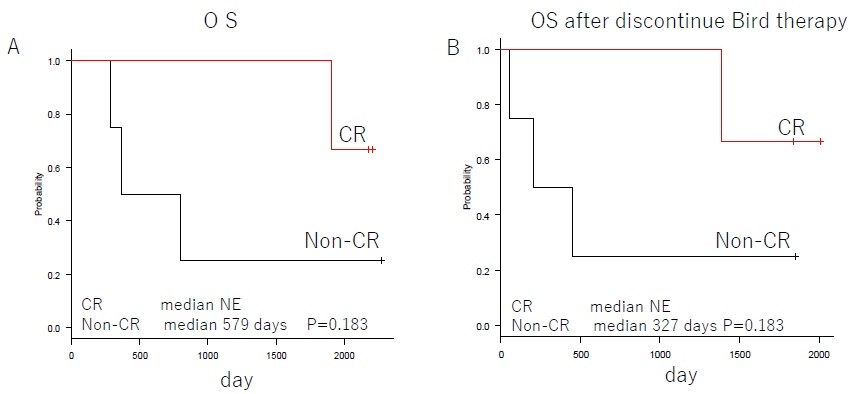
In the FIRST trial for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, the 4-year OS of Ld continues group was 59%.3 Asher A et al. reported that the response rates of PR or better for Ld therapy on relapsed refractory multiple myeloma patients were 60.9%, 54.2%, and 69.8% for age groups 64-years and younger, 65-74-years, and 75-years and older respectively. The median survival rates were 43.9-months, 33.3-months, and 34.3-months respectively.12 The results of our study indicate that the 4-year OS was 57% (Figure 2). This is the same as the 4-year OS reported by the FIRST trial, and it indicates sufficient efficacy since it includes relapsed refractory patients. The overall response rate was 86%, indicating a satisfactory result. In addition, the median survival rate for patients who were able to undergo at least 10 cycles tended to be satisfactory, at 4202-days (p-0.319) (Figure 3). The best therapeutic effect in patients with CR or above did not reach the median value (Figure 4). The duration of response was 316-days (range, 160-522), but the survival rate was satisfactory. These findings are related to the fact that the OS after discontinuation of Bird therapy was satisfactory, at 1,385-days. Recently, survival post-progression (SPP) has been gaining attention.13 This indicates that even when the PFS for the prior therapy was satisfactory if the subsequent treatment following relapse is poor, the overall survival rate is also poor. This is because, in contrast, even when the PFS for the prior therapy was not satisfactory if the subsequent treatment following relapse is good, the overall survival rate will improve. Thus, it is difficult to extend OS when the subsequent treatment is poor, even in cases when the prior therapy is good. Therefore, it is necessary to select a prior therapy that does not have a negative effect on the subsequent treatment, and therefore particular care is required when treating elderly patients. We think that the results of Bird therapy were further extended OS by the effect of subsequent treatment in this study. Novel drugs for use following Bird therapy have been developed, and their use as a subsequent treatment that is not negatively affected by Bird therapy probably led to the good outcomes. In particular, patients that achieved CR or better as a result of Bird therapy had better survival rates after cessation of Bird therapy than patients who did not achieve CR. Combination therapy with Clarithromycin and Imids was first reported in 2002 by Coleman who also reported on combination therapy with Clarithromycin, Thalidomide, and Decadron (BLT-D). These drugs achieved an overall response rate of 92%, including 13% of CR, in cases of newly and relapsed multiple myeloma.14 Subsequently, Gay reported on their comparison of Bird therapy and Ld therapy on cases of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. They reported the following results indicating that CR was superior to Ld; 45.8%:13.9% of CR; 73.6%:33.3% of VGPR; 89.7%:73% of 3-year OS.15 Rossialso reported a 5-year survival rate of 75.2%9 and in an even more intriguing study, Ghosh reported that in patients with resistance to Ld who were administered Clarithromycin, 41.7% attained at least PR and the median survival period was 25-months. Thus, it is considered that even in Ld-resistant patients the additional administration of Clarithromycin may be effective.16 With regard to CAM, even in the report of Niesvizky, the average dose was 400 mg/day, and it is considered that even when CAM was 400 mg/day in the study, the effect was recognized from OS.10
Figure 3. Subgroup Analysis of OS in 10 Cycles or More and Less than 10 Cycles
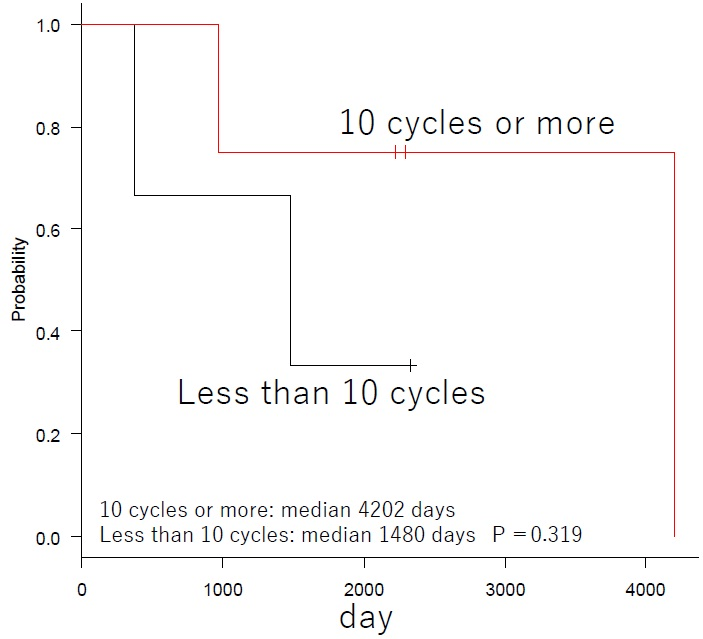
Figure 4. Subgroup Analysis of OS in 1CR and Non-CR. Panel A Shows OS of Bird Therapy. Panel B
Shows OS After Discontinue Bird Therapy. NE Denotes Could Not be Estimated
In terms of safety, as the mean dose of Len was low, at 16 mg, hematological adverse events were no problems with G1-2. Non-hematological adverse events were within the tolerable range. Although all patients who were administered Clarithromycin experienced liver dysfunction, it was of G1-2 and therefore could be controlled. Syncope was temporary and did not present problems with treatment. The patient with duodenal ulcer required fasting and pharmacotherapy, but this resulted in improvement, and Bird therapy could be resumed.
“In Japan, the starting dose is often reduced in the practice because of intolerable problems. We, therefore, reduced the starting dose in this protocol.” in the discussion part.
CONCLUSION
Bird therapy, which consists of additional Clarithromycin administration to patients whose Ld therapy does not have a satisfactory effect improves the response rate of Ld therapy. In addition, Bird therapy had few adverse effects and had little effect on post-relapse therapy. Therefore, after Bird therapy, sufficient treatment can be performed, and post-relapse therapy can obtain a good response and the duration of response to Post-relapse therapy becomes longer. For those reasons, we think that Bird therapy can improve overall survival. Bird therapy is considered to be effective from the antitumor effects of CAM and the concept of SPP. However, as this study included only a small number of patients, further study is required.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.









