The process of de-epithelialization in reduction mammoplasty surgery increases the operation time. In addition, longer operation times are more apt to cause fatigue for the surgeon. Furthermore, it is always preferable to use the time in the operating theater as effectively as possible. Although the gold standard when performing de-epithelialization is with the use of a scalpel, there are some initiatives to accelerate the speed of the operation and decrease the blood loss during the operation.1-5 While the use of novel products has the potential to speed up the operation, their use may be accompanied by unexpected complications.1,5
In our department, we use a ‘monobloc’ de-epithelialization method. After making skin incisions around the marked pedicle, the de-epithelialization starts from the submammarian fold and continues towards the nipple. The procedure can also be performed from the nipple to submammarian fold. The epidermal layer is removed as a whole. At the beginning of the process, 2 hemostats are clamped to apply traction. After enough of the epidermal layer is raised, it is perforated, and traction can easily be applied by hand. At the same time, the assistant applies pressure on the de-epitelized sides with an abdominal gauze pad so that blood loss can be decreased while the traction makes the de-epitelization process easier (Figure 1 and Video 1).
Figure 1: The de-epithelialization process starts from the mammarian fold and continues towards the nipple-areola complex.
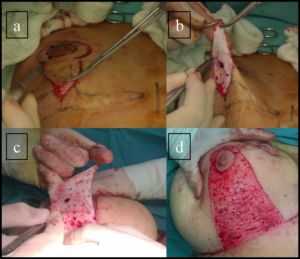
Video 1: The de-epithelialization technique.
Note: To best view
1. Kindly open the pdf file in Adobe Reader XI version.
2. Please save the pdf file on your local computer.
3. To watch the video kindly install the latest adobe flash player. Click here to download: http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer/otherversions/
When compared with the previous methods, this method has several advantages including:
- Ease of performance.
- Accurate excision of the epidermal layer.
- Decreased de-epithelialization time.
- Decreased blood loss.
We conclude that this modified method allows the surgeon to use his/her instruments more quickly and effectively, resulting in a decrease in the operation time and blood loss and can be adapted to such operations required de-epitelization.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
CONSENT
The authors obtained written informed consent from the patient for submission of this manuscript for publication.






