INTRODUCTION
The modern health boom has caused Nordic walking (NW) to become increasingly popular as a form of exercise in and around northern Europe. NW is a walking style that developed from summer time cross-country ski training and requires two ski poles.1
Many studies have reported that a difference between NW and normal level walking (LW) is the energy expenditure involved2,3,4,5,6,7; when NW and LW are conducted at a certain speed, oxygen uptake (V̇O2) and heart rate (HR) are higher in NW. The researchers conducting these studies concluded that the reason for this difference is that NW involves many muscles of the upper limbs.4,5,8 On the other hand, some researchers have reported that V̇O2 and HR increased in NW but perceived exertion did not. Figard-Fabre et al9 studied obese middle-aged women and found that perceived exertion was lower in NW than in LW at the same speed. In view of these results, we could regard NW as a suitable exercise style for health promotion, since it appears to offer higher exercise intensity with comparable or less perceived exertion relative to LW.
Nevertheless, it can hardly be assumed that NW would benefit everyone, as the exercise intensity of NW exceeds that of LW when the walker moves at the same speed. Higher exercise intensity would mean greater difficulty in performing the exercise for people who have a low physical fitness level, and this greater difficulty can lead to reduced motivation for exercise. Based on previous studies,2,5,6 it can be predicted that the intensity of NW will equal that of LW only when one performs NW at a slower speed than LW. However, no study has compared the effects of NW and LW when the exercise intensity is equivalent in both forms of walking. In addition, no study has been conducted while retaining the same relative intensity of V̇O2 between NW and LW. If relative intensity were the same, it appears that the speed, or absolute intensity, should differ. Thus, it is proposed that perceived exertion can be affected because of differences in the muscle groups involved between NW and LW. However, no research has tested this conjecture.
Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to clarify the relationship between perceived exertion levels in NW and LW when the relative intensity is equivalent.
METHODS
Subjects
The subjects were eight healthy male university students who exercise regularly. Their mean±standard error (SE) in age, height, weight, and maximal oxygen uptake (V̇O2max) are shown in Table 1. All subjects received a complete explanation in advance about the purpose of the experiment, its contents, and safety issues based on the Declaration of Helsinki and the guidelines of the Ethical Committee of Shizuoka University (approval No. 12-26) on studies indicated involving human experimentation; all subjects indicated their informed consent. Concerning NW training, all participants received, before performing the experiment, guidance from an instructor certified by the International Nordic Walking Federation (INWA), who explained the technique of NW and how to walk with the Nordic poles for a minimum of 30 minutes on a treadmill. The participants were asked not to drink alcohol and to get enough sleep before the experiment.
Table 1. Each Subject Characteristics
|
Subject
|
Age (year)
|
Height (cm)
|
Weight (kg)
|
V̇O2max (ml/kg・min)
|
|
A
|
24
|
179.6
|
60.6
|
63.9
|
|
B
|
21
|
180.9
|
79.6
|
60.6
|
|
C
|
21
|
168.0
|
58.2
|
57.2
|
|
D
|
19
|
174.7
|
68.5
|
56.1
|
|
E
|
19
|
163.5
|
65.5
|
59.5
|
|
F
|
19
|
174.9
|
70.7
|
66.3
|
|
G
|
20
|
177.0
|
78.4
|
61.6
|
|
H
|
20
|
186.2
|
72.3
|
61.9
|
|
Mean
|
20.4
|
175.6
|
69.2
|
60.9
|
|
SE
|
1.7
|
7.2
|
7.7
|
3.3
|
Experimental Protocol
Subjects entered the laboratory 30 minutes prior to the starting time of their experimental session. Then, after confirmation of their health condition, their height and body weight were measured.
The incremental test: Prior to the experiment, subjects performed an incremental test to measure their V̇O2max, which is an index of exercise intensity. After putting on the electrocardiogram (ECG) (ZS-530P, Nihon Kohden, Tokyo, Japan) electrodes, the subjects put on a ventilation mask and measured their resting metabolism while remaining in a sitting position on the chair for five minutes. They first started to walk at 60 m/min using the method of incremental loading. The speed increased gradually by 20 m/min every two minutes to 200 m/min. The subjects were to perform walking up to and including the speed 120 m/min, and then to begin running when the speed increased to140 m/min. The speed increased gradually by 10 m/min every minute from 200 m/min or until the participant became exhausted.
We developed a regression formula between oxygen uptake (V̇O2) and walking speed based on the results of each subject’s incremental test. We calculated each subject’s speed at 40% of V̇O2max as the desired exercise intensity for the Nordic walking condition; then, the subjects performed the submaximal exercise test of NW (the NW condition). Thereafter, we substituted the value of V̇O2 provided on the NW condition into the regression formula from the incremental test to obtain the speed at which the subject should walk in the level walking test (the LW condition). The subject then performed that test.
The exercise submaximal test for the NW condition and LW condition: For the measurement under each walking condition, subjects put on the ventilation mask and stepped onto the treadmill after putting on the ECG electrodes and their resting metabolism while sitting in a chair was measured for five minutes. Thereafter, subjects performed a warm up in LW at their 40% of V̇O2max speed for five minutes, and after an interval of three minutes they performed the condition exercise of NW or LW for six minutes. In the case of the NW test, the subjects put on the Nordic poles during the interval. The OMNI scale was administered before starting the six minutes of exercise, at the three-minute point, and immediately after finishing. The measurement of the NW condition and the LW condition for each subject took place on separate days.
All experimental measurements occurred in the laboratory, in temperature of 21.3±0.2 ºC and with humidity levels of 40.9±0.7%. All the experiments were conducted on the treadmill (made by Lode Company for athletice use), and the slope was set at gradient of 5%.
Measurement
The subjects’ V̇O2 level was measured every 30 seconds during the exercise and resting time. The measurement of the expiration concentration was conducted using a gas analyzer aeromonitor (AE-310S; Minato, Tokyo, Japan), which was tested with a known concentration (O2: 14.98%, CO2: 4.62%) prior to the experiment. At the same time, the expiratory volume was estimated by calculating the volume passing through a flow meter (HI-101; Chest, Tokyo, Japan) every 30 seconds, which is based on the Douglasbag method.
Four criteria were used to assess the point of exhaustion: (1) reaching plateau of V̇O2, (2) reaching the subject’s maximal perceived exertion, (3) a respiration quotient greater than 1.0, and (4) approaching the maximal heart rate (calculated as 220 minus the subject’s age). When three of these four criteria were satisfied, we defined the V̇O2 at that point as the subject’s V̇O2max.
V̇O2 in both conditions was calculated by taking the mean level during the last one minute thirty seconds of steady exercise for the six minutes. V̇O2 in both conditions converting it into a percentage of V̇O2 to be correlated between a percentage of V̇O2 and a heart rate reserve (%HRR).10 In addition, using a patient monitor (BSM-2401, Nihon Kohden, Tokyo, Japan), we recorded the ECG consecutively and counted an interval every one beat (R splinter-R splinter) for 30 seconds by calculating the value every minute so as to find the heart rate (HR) per minute. HR was calculated as the mean during the two minutes before the end of the measurement and was converted into %HRR.10
We measured the perceived exertion using the OMNI scale (eleven levels).11 We recorded it on the incremental exhaustion tests only with regard to the whole body; for both conditions of the experiment, perceived exertion was recorded for the whole body, upper limbs, and lower limbs.5 On the incremental test, we recorded perceived exertion immediately before the gradual increase in speed began; in both conditions, we recorded it before the exercise, at the three-minute point, and after the exercise. The statistical analysis refers to the value at the completion of exercise.
Statistics
We calculated the result of the measurements for all subjects in terms of mean±standard error (SE). We used SPSS software version 22.0 for Windows. The effects of all results were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) following the Bonferroni method. Significance levels were set at p<0.05 or p<0.01.
RESULTS
Incremental exhaustion test
The subjects’maximal heart rate (HRmax) and V̇O2max were 198.9±2.6 beats/min and 60.9±1.2 ml/kg/min, respectively. All subjects met at least three of the exhaustion criteria before completing the test.
The exercise submaximal test for the NW and LW condition
The NW condition was conducted at 40% of V̇O2max speed (94.4±1.8 m/min) as specified by the incremental exhaustion test. As a result, V̇O2 was significantly higher than the estimated value provided by the incremental test, by the amount of 11.3±3.7% (p<0.05). The percentage of V̇O2max and the speed attained on the submaximal exercise test were 38.1±3.5% and 94.4±1.8 m/min, respectively, on the NW condition and 41.3±2.4% and 105.1±3.2 m/min on the LW condition, respectively (Figures 1-A and 2). Although there was no significant difference in V̇O2, there was a significant difference in speed of 10.7 m/min (p<0.01). In addition, no significant difference was found in %HRR, as in V̇O2, between the NW condition (44.5±1.5%) and the LW condition (44.0±2.7%) (Figure 1-B).

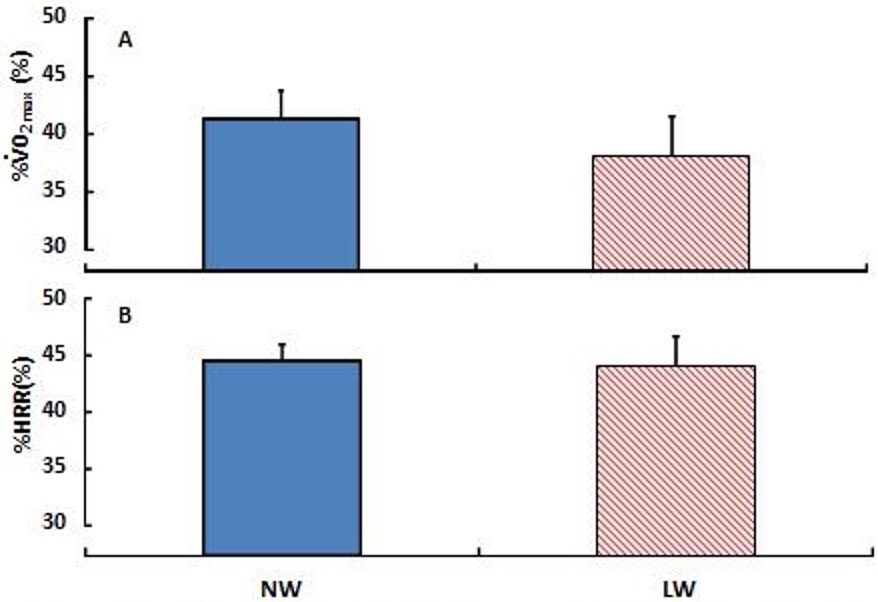
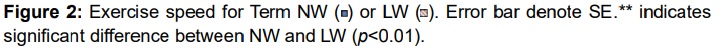
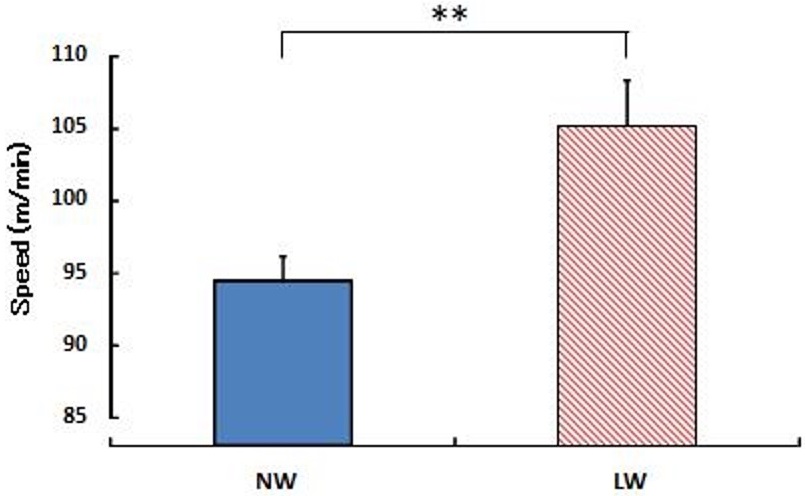
Figure 3 shows the OMNI scale results at the completion of exercise with regard to the whole body, upper limbs, and lower limbs in that order. Concerning the whole body and the lower limbs, there was no significant difference between the conditions: 2.0±0.4 (whole body), 1.4±0.3 (lower limbs) on the NW condition and 1.3±0.6 (whole body), 2.3±0.8 (lower limbs on the LW condition. On the other hand, the NW condition showed a significantly higher value than the LW condition for the upper limbs (NW: 3.3±0.6, LW: 0.4±0.2) (p<0.01).

 DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
The purpose of the present study was to compare and investigate V̇O2, HR, and perceived exertion by implementing exercise tests under the two terms, Nordic walking and level walking, when V̇O2 was equalized between two conditions as a measurement of the relative exercise intensity.
In this study, subjects performed at the intensity level of 40% of V̇O2max, which improves cardiorespiratory fitness12 and is the walking pattern most commonly used in NW. The growth rate of V̇O2 under the NW condition at the speed defined as 40% of V̇O2max speed increased by 11.3% (p<0.05). When the LW condition was conducted in accordance with this increased V̇O2, the speed in the LW condition was, on average, 10.7 m/min greater than that in the NW condition (p<0.01). There was no significant difference between the conditions with regard to %V̇O2 and %HRR. Moreover, to perform the LW condition at a perceived exertion level equivalent to the NW condition, the required speed in the LW condition was faster than that required at 40% of V̇O2max. Therefore, NW exercise intensity is equal to that of LW at an NW speed of about 10 m/min slower.
Based on previous studies, we expected that if exercise intensity was equivalent in both conditions, the LW condition would increase perceived exertion.3,9 However, the whole-body OMNI scale did not show a difference between the two conditions in the present study. The experimental speed in the present study was equivalent to approximately 90-110 m/min. Thus, integrated electromyogram (iEMG) in the lower limbs of NW was significantly lower in the vastus lateral is and gastrocnemius muscle at this range of speed, as noted by Sugiyama et al5 In other words, it is likely that the difference might have reduced the burden on the lower limbs on the OMNI scale. It is also said that the burden on the knee joint is reduced in NW.13 However, no difference was found in the lower limbs on the OMNI scale in this study since subjects’ physical fitness levels were high. For subjects in this study, the NW condition was the speed of 40% V̇O2max and LW condition was that of approximate 51.3% V̇O2max that was equivalent to fast walking. Thus, it was unlikely to perceive fatigue as for the speed of 40% V̇O2max -approximate 50% V̇O2max for six minutes using large muscles of the lower limbs. If untrained or aged subjects performed the NW and LW condition in this study, the lower limbs on the OMNI scale of the NW condition would be lower than that of the LW condition. On the other hand, NW is significantly higher than LW in iEMG of the arms at all speeds and a conventional or uphill slope.5,8,14 As for the upper limbs on the OMNI scale in the present study, the burden on the upper limbs was significantly higher in the NW condition due to the use of Nordic poles. Schiffer et al4 reported that blood lactic acid concentration in NW becomes higher than that in LW. It would seem that a lactate increase is unlikely to happen at the intensity of 40% of V̇O2max, but because the OMNI scale score for the upper limbs is high, catecholamine release due to the arm exercise,15 which represents an early increased expenditure of V̇O2, may be large. In this way, it is possible that subjects would generate lactic acid accumulation. In that case, the lactic acid produced in the arms includes the possibility of a lactic acid shuttle that is reused as energy in the lower limb exercise through the blood. As for V̇O2, Povop et al16 reported that an aerobic threshold (AT) was reached earlier in exercise that involves the upper limbs by using poles than in running exercise. Additionally, the activation of the sympathetic nerve because of the mobilization of the muscles in the upper limbs increases the cardiorespiratory function, and this is presumed to increase V̇O2. In contrast, because the LW condition at the equivalent speed to the NW condition mainly involves exercise of the lower limbs, the cardiorespiratory action in the LW condition is slower than that in the NW condition since the increase of catecholamine is slower. However, because the amount of change in the central circulatory system is larger during lower-limb exercise, it is thought that the reply using the arms in NW might be equal to the increased burden placed on the lower limbs of LW. This possibility is indicated by the lack of significant difference between NW and LW for the whole body on the OMNI scale.
In future studies, by using subjects who are more accustomed to exercise at intensities of 40% to 60%, we may find greater differences between the two terms. We could confirm more than fourth level of OMNI scale on the upper limbs of the NW condition despite 40% V̇O2max in this study. Moreover, this is the new knowledge that there is the unique point which NW effects small muscles such as the upper limbs despite the low intensity. If low or moderate intensity of NW increase V̇O2 by 11.3%, it may be possible to get exercise whose intensity is near the 40% V̇O2max from NW which is actually set to 28.7%V̇O2max. After this, if NW was compared with LW at the same relative intensities based on previous studies7,17 that LW was improved V̇O2 or HR and so on for those who were untrained or aged, it would be clearer evidences of beneficial NW. In other words, NW may be very appropriate regarding a promotion of health. Moreover, we may be able to identify more clearly the physiological characteristics of using Nordic poles by focusing on the sports level or intensities of 70% of V̇O2max or more.
Eventually, we would like to gain a better understanding of the characteristics of NW by examining subjective perceptions of NW and LW intensity in exercise at various exercise intensities over longer periods of time.
CONCLUSION
Our study has shown that, in NW with equal relative exercise intensity to that of LW performed on a treadmill, V̇O2 and HR increased even with slower walking speed. In other words, it is necessary to perform LW exercise at a speed faster than NW in order to attain exercise of equivalent intensity. Only in the arms was perceived exertion during NW reported as higher; there was no significant difference with regard to exertion of the lower limbs or the whole body.
AUTHORS’CONTRIBUTIONS
Significant writing of the manuscript: KT, KS, HO. Concept and design: KT, KS. Data acquisition: KT, KS, EM, YS. Data analysis and interpretation: KT, KS, YS, HO. Statistical expertise: KS. Significant manuscript review and revisions: KS, HO. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We appreciate the kindness of all the subjects who participated in this study.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
There are no conflicts of interest to disclose.



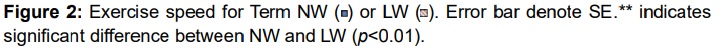

 DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION



