INTRODUCTION
Tuberculosis (TB) disease is commonly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 1 The higher incidence and prevalence of TB is a common health problem in developing countries.1 The bone structure particularly dorsal spine is the most common extrapulmonary area for TB after lymph nodes.1 The first modern description of spinal TB was defined by Sir Percival Pott in 1779.2 However rare condition, spinal TB still appears even in both developing and developed places.2 Spinal TB usually represents at advanced levels and diagnosis of this disease is not easy; the late diagnosis and management of disease cause to higher rates of spinal cord compression and deformities.2 Patients with spinal TB usually represent with gibbus formation, back ache, low grade fever, neurological symptoms and decificts.1 Herein, we would like to present an unusual case of cervical spine TB with neurological deficits and its management.
CASE REPORT
A 62-year-old man admitted to emergency department with paresthaesia, weakness and numbness in hands and feet in the past five days. These symptoms were insidious at onset and increasing gradually. He was under tuberculosis treatment (Isoniazid, Ethambutol, Pirazinamide, Rifampicin) and diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis two months ago. He also had a low-grade fever, which was relieved with medication. His vital signs were as follows; blood pressure 100/60 mmHg; body temperature 37.7 °C; heart rate 115 beats/min. On physical examination, he was oriented, alert and conscious. Bilateral upper extremity muscle strength was 3/5 proximally and 2/5 distally. Bilateral lower extremity muscle strength was 2/5 proximally and 1/5 distally. He also had global hypoesthesia on lower and upper extremities. Achilles clonus and plantar reflex were bilateral positive. Deep tendon reflexes were hyperactive on upper and lower extremities. He had an increment with white blood cell (WBC) and C-reactive protein (respectively 14.9-10*3/mm3 and 7.85 mg/dL). A destructive paravertebral abscess that was located lower cervical vertebrae was determined on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Shows that Paravertebral Abscess that was Located Lower Cervical Vertebrae on MRI.
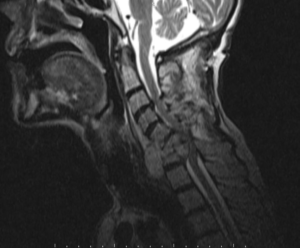
C5-C7 vertebrae corpectomy and abscess drainage were performed by neurosurgery and he was discharged nine days later. Objections of deadness and pain in the hands and feet of patient who is without neurological deficit has been continuing for eight months.
DISCUSSION
In many parts of the world, TB is still a growing health problem particularly in developing countries and also increasing in developed countries.3 This disease is one of the leading infectious situation in the world and is responsible for more than 2 million deaths.6 The incidence of spinal TB with neurological involvement is between 12.5-100% and it commonly leads to neurological sequelae if not treated sufficiently.3,4 Spinal TB in especially responsible for 1-3% of all TB cases and accounts for 40% of all spine infections.2
Because of the slow growth rate of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis, isolation, identification, and drug susceptibility testing of this organism can take several weeks or longer.6 Many molecular methods have been developed for direct detection, species identification, and drug susceptibility testing of this organism and these new methods can potentially reduce the diagnostic time.6 In recent years, two nucleic acid amplification methods, the Enhanced Mycobacterium tuberculosis Direct Test (Gen-Probe) and the Amplicor Mycobacterium tuberculosis Test (Roche Diagnostic Systems), have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for direct detection of M. Tuberculosis.6 PCR-based sequencing has become commonly used to identify many mycobacterial species and DNA probes have been widely used for species determination of the most commonly encountered mycobacteria.6
Although, commonly seen in dorsal spine lesions, cervical and cervico-thoracic lesions with spine TB rarely seen in literature and these cervical-upper thoracic spinal cord lesions with TB are prone to be compressed.4 In our case, spine TB abscess was located in lower cervical paravertebral area. Hu et al reported a 43-year-old man with a huge retropharyngeal abscess causing airway and esophageal obstruction associated with cervical spine TB and also they indicated that cervical spine TB is a rare condition, accounting for 3-5% of spinal TB.5 Alam et al reported a 38-year-old female with Pott’s C6 and C7 quadriparesis with bowel bladder involvement in their multi-center study.2 Her pretreatment MRI demonstrated destruction of C6- C7 vertebrae and compression of spinal cord. Anterior surgical decompression by corpectomy was performed to her.2 After four months, she was able to regain movement with relieved pain. In the follow-up period, there was no recurrence of TB. Conservative first line therapies treatment such as anti-TB drugs, anti-TB chemotherapy and surgery are treatment options of spinal TB.2 Surgical procedure should be considered patients with extensive spine involvement, severe deformity, vertebral body collapse, prevertebral cervical abscess, advanced neurological involvement and any sign of progressive recovery despite of conservative therapy.2
In conclusion, physicians must be aware about patients with neurological symptoms and deficits. The physician carefully should examine medical history and drug utilization of patients. It should not be forgotten that TB disease is common in particularly developing countries like Turkey.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
CONSENT
Oral consent has been taken from the patient.






