INTRODUCTION
Patient health and the reduction of risk of surgical site infections (SSIs) are of paramount importance in the operating room (OR) and a low temperature in the OR limits SSI rates dramatically, slowing the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. Technical standards on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning have been established to control OR air quality and thereby reduce risk to patients. Numerous organizations have contributed guidance to these standards, including the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), the American Society for Healthcare Engineering (ASHE), the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, and the Association of peri-Operative Registered Nurses (AORN).1 In 2019, the Joint Commission noted that 68-75 °F (20- 24 °C) is appropriate for the OR depending on the OR class.2 To ensure observance, the Joint Commission monitors institutions with regular unannounced surveys of their ORs.3 Though this temperature guidelines is higher than the ANSI/ASHRAE/ASHE Standard 170-2017 design guidance that ORs should be kept at between 66-68 °F (19-20 °C) and 30-60% humidity.4
And while taking every precaution to ensure that SSI risk is as low as possible in the OR and that the scrubbed-in surgical staff are comfortable, it has been observed that the low temperature has a negative effect on the performance, comfort, and well-being of surgical staff working peripherally, including peri-operative nurses, anesthesia providers, and perfusionists.5,6 To address this issue, several devices have been invented or repurposed to serve the thermal comfort needs of the OR staff. Two such popular devices are the off-label use of the 3MTM Bair HuggerTM Patient Normothermia System and OPERATIONHEATJAC® products. The Bair HuggerTM is intended to be used to keep a patient’s core body temperature within the normothermic temperature zone while they are on the operating table.7 However, it is often used by surgical staff for personal warmth wherein the hose attached to the Bair HuggerTM is diverted from the disposable Bair HuggerTM blankets and into the personal garments or blankets of the OR staff. This method is not AORN compliant as it introduces contaminated air flow into the OR.
OPERATIONHEATJAC® products are heated garments worn over scrubs, but under the outer surgical layers, such as a scrub warm-up jacket or surgical gown.8 Garments are launderable and include belts that wrap around the midsection and vests. A number of options are available for powering the garments, including rechargeable batteries, plug-in transformers, and air activated warmers. They are AORN compliant and meant to be worn unexposed.
While these devices have the potential to successfully warm and increase the comfort of surgical staff, the principal goal in the OR of protecting patient health requires that any devices that are used be examined critically to be certain that no additional risk to the patient is being added by its use.
In this study, we compared off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM with that of the OPERATIONHEATJAC® transformer only (TRO) in a simulated OR using blood agar and counting the bacterial contamination that resulted over time. We then compared the existing literature to determine the importance of comfortable staff and the ramifications this has on hospitals and patients.
Statement of Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the direct association between bacteria growth in a control compared with two commonly used warming devices: the off-label use of the forced-air patient warming device, the Bair HuggerTM, and the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO. We will also analyze the importance and feasibility of staff comfort in the OR based on research previously conducted.
Research Questions
A number of questions motivated us to begin this research. First, does the off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM device result in higher levels of bacteria growth compared with scrubs alone? We also seek to determine whether the use of the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO warming device results in higher levels of bacteria growth compared with scrubs alone? Secondly, does the amount of time a device is in use contribute to higher bacteria growth when these devices are in use? Finally, how does the existing literature shape or alter the value of these data?
Statement of Significance to Nursing
While the comfort of the OR staff is important, it is critical that no additional risk is added to the OR by comfort devices. A detailed analysis of the potential contamination caused by the use of the off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM and OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO is necessary before they should be used in a live OR.
METHODS
The objective of this study was to observe whether the offlabel use of the Bair HuggerTM or the appropriate use of the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO can increase and cause the spread of bacteria in the OR.
To test this theory in a non-biased manner, the author enlisted a Contract Research Organization that specializes in recreating studies that require a mock, but realistic OR environment. The experiment and preliminary results were blinded until they had been analyzed. As this study was investigational and the potential for harm to patients is unacceptable, it was conducted in a mock OR without the presence of a patient. As such, it did not require Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval.
Study Design
The mock OR was set to 68 °F (20 °C). Air did not circulate in the area during or 24-hours prior to the experiment. Humidity was set to 30%. Testing periods were established at three and six hours for the three comparators with three active participants for a total six rounds of the experiment. In the first three rounds of the experiment, participants remained in the OR for three hours. For the three-hour control phase, 30 agar plates were placed around the OR at or about one meter above the ground and one meter from the wall in various positions around the test area. No staff warming devices were used during this phase.
The off-label use of the 3MTM Bair HuggerTM Normothermia System was tested next.9 In this portion of the experiment, the participants would place the Bair HuggerTM in various positions in their scrubs, including the top and bottom. They were permitted to move the hose attachment as they preferred to simulate real life use. Thirty blood agar plates were placed around the room as noted in the control tests.
Finally, the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO electric heated garment was tested in the same manner as the control and comparator group.10 Participants wore the garment as noted in the instructions for each duration.
Each round of the experiment was repeated once more for a period of six hours. In all rounds of this experiment, the participants functioned regularly, conducting basic surgical staff duties, including preparing equipment, making notes, and other small functional and cognitive tasks. Participants wore scrubs and scrub jackets during all rounds of the experiment. Between phases of the experiment, the area was sanitized.
At the end of each phase of the experiment, the agar plates were removed, labeled with a sample number, and dated. These plates were incubated at 98.6 °Ft (37 °C) for 24-hours. Once incubation was complete, each was observed for growth and number of colonies per plate were counted. The colony forming unit (cfu) count/plate is expressed as cfu/m3 by the Omeliansky formula.
Cfu data were analyzed using a two-sided t-test using statistical analysis software (SAS) 9.4. A probability of p<0.05 considered significant.
RESULTS
Agar plates were consistent with their respective groups in both the three and the six-hour experiments (Figure 1). No outliers were noted.
Figure 1. Findings for All Plate Readings
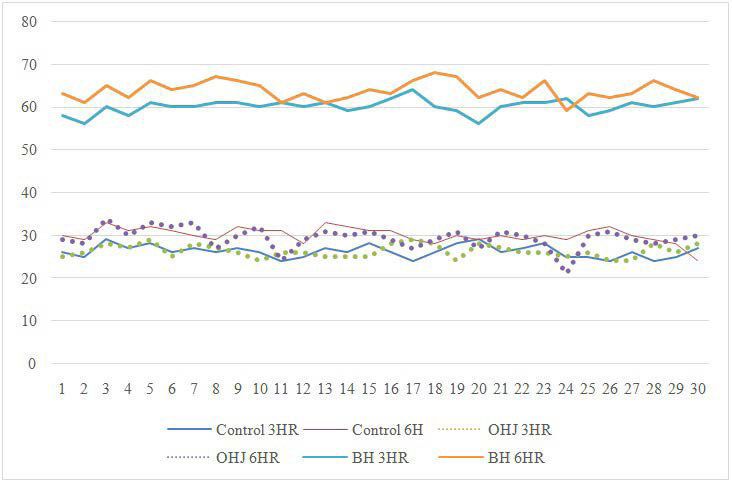
Three-Hour Experiments
The control plates had a mean cfu/m3 of 26.233 (standard deviation [SD]: 1.431 cfu/m3 ), which was very similar to the plates in the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO tests (mean: 26.300 cfu/ m3 ; SD: 1.535 cfu/m3 ). As such, there was no significant increase in the cfu rate in the air for the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO plates compared with the control plates (95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.700 to 0.833 cfu/m3 ; p=0.862).
The mean cfu for off-label use Bair HuggerTM plates was notably higher than the control group at 60.07 cfu/m3 (SD: 1.701 cfu/m3) and a statistically significant increase in the cfu rate in the
air was noted (95% CI: 33.021 to 34.646 cfu/m3; p<0.001).
Compared with the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO, the off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM produced a 43.78% higher cfu rate in the three-hour phase of the experiment (Table 1).
| Table 1. Three Hour Experiments t-Test Results |
|
Test
|
Mean |
SD |
Compared with Control |
| 95% CI |
p-Value
|
| OHJ |
26.300
|
1.535 |
-0.700-0.833 |
0.86245
|
| BH |
60.067 |
1.701 |
33.021-34.646 |
<0.0001
|
| CONTROL |
26.233
|
1.431
|
|
|
| BH: 3MTM Bair HuggerTM; CI: Confidence Interval; OHJ: OperationHeatJac®; SD: standard deviation |
Six-Hour Experiments
As with the three-hour experiments, the six-hour experiments showed that the off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM produced a greater rate of cfu on average (46.18%) (Table 2).
| Table 2. Six Hour Experiments t-Test Results |
|
Test
|
Mean |
SD |
Compared with Control |
| 95% CI |
p-Value
|
|
OHJ
|
29.433 |
2.622 |
-1.799-0.533 |
0.28145
|
| BH |
63.733
|
2.164 |
32.634-34.700 |
<0.0001
|
| CONTROL |
30.067
|
1.818
|
|
|
| BH: 3MTM Bair HuggerTM; CI: Confidence Interval; OHJ: OperationHeatJac®; SD: standard deviation |
In this situation, the use of the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO actually resulted in a lesser cfu rate compared with the control (29.43 [SD:2.622] cfu/m3 vs 30.67 [1.818] cfu/m3), however, the difference was not statistically significant (95% CI: -1.799 to 0.533cfu/m3; p=0.2501).
The off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM produced a cfu rate in the air slightly higher than in the three-hour experiments (63.733 cfu/m3 vs 60.07 [SD: 2.164] cfu/m3). A statistically significant increase in the cfu rate in the air was also noted in this timeframe compared with control (95% CI: 32.63 to 34.70 cfu/m3;p< 0.001).
DISCUSSION
This experiment shows that the incorrect use of a device has the potential to cause serious harm to patients. Hospitals are constantly fighting infection rates to help protect patients. Numerous examples in the literature have analyzed SSIs for the toll they take on patients11-13 and for their financial impact on the healthcare system.14-16
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection, SSIs occur in 2-4% of all patients undergoing inpatient surgical procedures and are a prominent cause of morbidity and mortality after surgery.11 In a study which reviewed nearly half a million operations to follow 30-day readmission rates following surgery at a single hospital, readmissions due to SSI accounted for the largest proportion of overall admission.17 Most alarmingly, 3.0% of patients who contract an SSI die as a consequence.
A 2019 retrospective index analysis of hospital costs from inpatients harms estimated that SSIs cost an average of $32,000 per incidence.18 When the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) stopped paying for care related to preventable hospital-acquired conditions in 2008, these costs transferred from insurers to the hospitals, adding an average of $21 million dollars in costs over a three-year period to a single center.
Considering these two large pressures hospitals face, it is hugely important that risk in the OR be minimalized as much as possible. As our data have shown, the incorrect use of a medical device for self-warmth leads to the production of more bacteria and can increase SSIs and endanger both the well-being of patients and hospital financial stability. However, hospitals should not just ignore these data and disallow all staff warmth equipment in the OR. Instead, hospitals must look closely at the current literature to realize that eliminating all staff warming devices outside of scrub jackets is far from the most appropriate option to protect patients and minimize risk. In fact, providing options for warmth that do not increase risk may save time and money for hospitals.
An assessment of the environmental comfort in an OR from the American Industrial Hygiene Association noted the complexity of both sides of surgery: the patient and the surgical team, who have very different needs.6 The pilot study worked in an orthopaedics OR measuring several physiological parameters and the comfort of each staff member. Of the eight-person staff, the two surgeons were generally rated as “hot” or “very hot.” The surgical assistants were mostly “hot” and “slightly hot.” And finally, the nurses were “comfortable” 75% of the time and “cold” 20% of the time. This study is one of few that demonstrate how diverse the needs of the staff are and follows with the assumption that staff members who play a more physically rigorous roles in the OR are warmer, while those will less physically demanding roles tend to be cooler. A limitation of this study that keeps the information from being wholly authentic to the entire surgical staff is the lack of an anesthesia provider.
A similarly designed study from Canada studied the thermal environment in two ORs, evaluating the thermal comfort of the staff based on environmental measures during surgeries and with questionnaires.19 As with the above trial, it was noted that surgeons tended to feel from “slightly warm” to “hot”— sweating often throughout surgery—and anesthesia providers and nurses tended to feel from “slightly cool” to “cold.” Using Fanger’s predicted mean vote (PMV) model, which assumes a uniform thermal environment, the air temperature in the OR was thermally comfortable to the surgeons at 66 °F (19 °C), while at that temperature, nurses and anesthesia providers would have to be clothed with at least 0.9 clothing (clo) to be comfortable, which is roughly six additional pounds of clothing.
Finally, the first study to report on the thermal comfort of the surgical staff reported nearly identical results, suggesting an increase in clothing for non-sterile staff to help with thermal discomfort.5 However, the age of this study and the developments that the OR has since seen have progressed far enough that its detailed inclusion does not add value to the literature review.
While a considerable amount of research has been done analyzing the effect of OR temperature on patients and there are a few meaningful studies on the benefits of thermal comfort for OR staff, numerous, high-quality studies outside of the OR have detailed the difficulties workers have in uncomfortably cold environments. These do well to flesh out the importance of a comfortable work environment.
A 2019 study aimed to investigate the effect of air temperature on the executive functions of the human brain and body physiology responses.20 The study found that unfavorable air temperatures may have a considerable effect on physiological responses and the cognitive functions among those working indoors. The moderate (70 °F [21 °C]) and low (66 °F [19 °C]) air temperatures had a very profound effect on changes in heartbeat rate, the accuracy of brain executive functions, and the response time to stimuli. Accuracy by different workload levels and various air temperature conditions were statistically significant (p<0.05). The ratio between low frequency and high frequency and the respiratory rate were more profoundly affected in the lower air temperatures than the moderate air temperatures (p<0.05).
A 2019 PLoSOne observational trial evaluated 543 individuals and found that the effects of temperature varied significantly for women.21 In temperatures of less than 68 °F (20 °C), women were more likely to score lower at math than men, while at higher temperatures, women outperformed their male counterparts. This raises an interesting question for the issue of comfort in the OR.
Two meta-analyses evaluating the effect of temperature exposure on performance found that, among the combined >50 trials included between the two, psychomotor and perceptual task
performance were most degraded in cold temperatures.22,23 The older of the two found that cold temperatures of 50 °F (10 °C) or less resulted in the greater detriment in performance compared with neutral temperatures by 13.91%. They also went on to analyze the effect of duration of exposure, finding that the longer an individual is exposed to the cold prior to the task onset, a greater differential effect on performance existed.
There is a significant amount of work done analyzing the effect of cold on staff outside of the OR but newer, more credible materials is needed for inside the OR; it is necessary that certain explorations be made to understand a situation in which substantial amounts of research have not been conducted. Given the existence of the paradox that a cold OR is necessary for surgeon comfort and resulting patient safety, but that very cold itself impedes surgical and anesthesia personnel and increases risk to the patient is a problem that requires more attention from researcher and hospital administrators alike.
LIMITATIONS
This study is limited in two main ways: the experiment was performed in a mock OR environment. While this was the responsible decision given that we theorized the off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM would increase colony forming unit (cfu) rates and potentially put patients at an increased risk for SSIs, it was not a live experiment. In the future, this experiment should be repeated without the off-label use of the Bair HuggerTM in active surgeries in a larger format with more comparators. Finally, there is a lack of quantitative research from the literature review portion of this article, as such there were numerous avenues of interest, particularly with the staff satisfaction surveys, that could not be explored. The solution is to encourage investigators to produce more research on the effect of temperature on the staff in the OR in a manner than will not increase risk to patients, such as surveys, physiological exams, and biosensors.24
RECOMMENDATIONS
Recommendations for Clinical Practice
The author recommends that clinicians explore medical devices that will increase clinician comfort and satisfaction in the OR. These devices must be AORN compliant and must not increase the risk of SSIs to the patient.
Recommendations for Education
This article serves as an excellent example for OR staff and hospital administrators to understand that there may be an unforeseen risk in the devices they use and that careful thought must always go into selecting any personal garments for the OR. It is also important that clinicians know that there are devices on the market that can make them more comfortable without increasing risk to the patients.
Recommendations for Future Research
Additional research into the level of morale in the OR with quantitative data is necessary to better understand the environmental issues in the OR from the perspective of the staff. We must also work to develop and adopt solutions that can increase staff comfort in the OR and potentially improve patient outcomes.
CONCLUSION
While of number of devices exist to warm and increase the comfort of the OR, it is important to always be as certain as possible that the comfort of the staff does not increase risk to the patient. The off-label use of the forced-air warming device, the Bair HuggerTM, significantly increased the average cfu rates in the air compared with the control at three and six hours. With the OPERATIONHEATJAC® TRO, there was no statistically significant increase in the average cfu rate in the air compared with the control at three or six hours. Staff warming devices must be chosen carefully to comply with safety standards. With many different staff members all serving crucial positions in the OR, it is possible for all members to be comfortable—but never at the expense of the patient’s safety.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to acknowledge Wilson Carroll Research Services, LLC for their assistance in conducting this study.
FUNDING SOURCES
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The research in this paper was conducted by an independent “paid for” CRO, Wilson Carrol Research Services, LLC, after the author conducted his own “home grown” research which demonstrated a bacteria colony count of 53 vs. 21 in the control, for a 121% increase in bacteria colony count from placing the hose of 3MTM’s Bair HuggerTM under his scrubs. The author was prepared for closing up shop if the findings were not significant. In an effort to improve medical care worldwide, the author believes this study is very significant. As the owner of the company HEATJACTM, LLC, the author has a vested interest in providing an alternative for OR staff to maintain comfort. If worldwide there is a reduction in SSIs and the associated misery, the author has achieved his goal. The author hereby declares there are no conflicts of interest whatsoever.






